* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
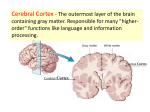
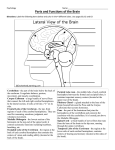
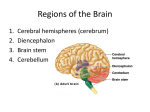
The Brain “For I know the thoughts that I think toward you, says the LORD, thoughts of peace and not of evil, to give you a future and a hope.” Jeremiah 29:11 [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous system • 1) cerebrum: upper part of brain; coordinates thought, memory, and learned behaviors • 2) cerebellum: lower part of brain; helps control balance and coordinate voluntary muscle activity • 3) brain stem: part that connects spinal cord; controls involuntary activities and activities of autonomic nervous system • weighs about 3lb. • Approximately 100 billion neurons each linked directly to about 100,000 others forming more than 10 quadrillion connections Cerebrum • helps in areas of consciousness, memory, voluntary actions, thinking, intelligence • right and left hemispheres split by longitudinal fissure • [Fig 8.14 p.130] • R hemisphere L hemisphere connected to L side of body connected to R side of body creativity details intuition logic/known procedures • corpus callosum: means of communication between hemispheres; mass of nerve fibers located at the base of the cerebrum • cerebral cortex – outer layer of cerebrum; gray matter made largely of cell bodies which lack myelin, located largely in the cerebral cortex; cerebral cortex consists mainly of nerve bodies located in a thin layer less than 3mm thick with axons projecting to interior of cortex; cortex deeply grooved making it possible for maximum amount of gray matter to fit in limited space • white matter lies in interior and consists largely of myelin covered nerve fibers; messages originating in cortex travel to other areas of brain; impulses from sense organs travel along white nerve fibers to cerebral cortex • lobes: regions that corresponds to major bones in the cranium; each body part controlled by a specific location on a specific lobe; each hemisphere has its own lobe • [Fig. 8.16 p. 132] • 1) frontal – personality, judgement, self-control; motor area controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles • 2) parietal – located behind frontal lobe; feel sensations such as temperature, pressure, and pain; shape, texture • 3) occipital – sense of vision • • 4) temporal – hearing, taste, smell cerebral palsy: damage to the cerebral motor area; intellect not affected Cerebellum • second largest brain region; located behind brain stem and just below occipital love of cerebrum; tissue is organized as white and gray matter; smaller convolutions • function – to coordinate skeletal muscle activity; cerebellum trained by cerebrum to operate muscles habitually; most complex muscle coordination handled by the cerebellum Brain Stem • located between cerebrum and spinal cord; all nerve fibers which connect the brain and the spinal cord must pass through it • medulla oblongata: lowest part of brain stem; nerve centers monitor and regulate breathing, heartbeat, blood pressure, swallowing, sneezing; all major sensory and motor pathways between body-cerebrum cross over here • pons: “bridge”; links cerebrum and cerebellum; assists medulla oblongata in regulating breathing; helps coordinate some eye movements and facial expressions • midbrain: above pons; help coordinate movements of both eyes, adjusts size of pupils in response to light, operates lens muscles to focus eyes on objects • reticular formation: master switch of the cerebrum; controls consciousness; constantly adjusts alertness level in response to senses and feedback from cerebral cortex; damage causes coma Limbic system • brain structures clustered around brain stem at core of the brain, surrounded by cerebrum; involved in coordinating different brain activities • thalamus: routs activation from reticular formation/sensory impulses to cerebral cortex • hypothalamus: control unit for body's autonomic systems; controls autonomic system (through brain stem) and endocrine system (through pituitary gland); also responsible for physical effects of emotions (hunger, thirst) • hippocampus: processes factual memories for storage • amygdala: helps generate emotions and process emotional memories Mind and Brain Connection • behaviorism: philosophy that behavior is determined by environment • Christianity: man also has spiritual component which influences thought and behavior Homework Section 8.3 #1-4 Section 8.4 #1-4