* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Reading - Red Hook Central Schools
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
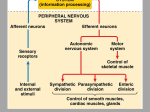
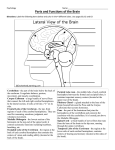
Name ______________________________ Class__________________ Date__________________ Skills Worksheet Active Reading Section: Human Body Systems Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. The brain consists of three major parts—the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. The capacity for learning, memory, perception, and intellectual functioning resides in the cerebrum. The cerebrum has a folded outer layer with many bumps and grooves. A long, deep groove down the center of the brain divides the cerebrum into right and left halves, or hemispheres. The cerebral hemispheres communicate through a connecting band of axons called the corpus callosum. In general, the left cerebral hemisphere receives sensations from and controls the movements of the right side of the body. The right cerebral hemisphere receives sensations from and controls the movements of the left side of the body. Most sensory and motor processing occurs in the cerebral cortex, the folded, thin (2–4 mm) outer layer of the cerebrum. The cerebral cortex contains about 10 percent of the brain’s neurons. The folded outer surface of the cerebrum is the cerebral cortex, which has a large surface area. The cerebral cortex is primarily involved with the functioning of sensory systems. Cerebellum: The cerebellum, which is located at the posterior base of the brain, regulates balance, posture, and movement. The cerebellum smoothes and coordinates ongoing movements, such as walking, by timing the contraction of skeletal muscles. The cerebellum integrates and responds to information about body position from the cerebrum and the spinal cord to control balance and posture. Brain stem: At the base of the brain is the stalklike brain stem. The brain stem is a collection of structures leading down to the spinal cord and connecting the cerebral hemispheres with the cerebellum. The lower brain stem consists of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. These structures relay information throughout the central nervous system and play an important role in homeostasis by regulating vital functions such as heart rate, breathing rate, body temperature, and sleep Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 8 Homeostasis and Human Body Systems Name ______________________________ Class__________________ Date__________________ Active Reading continued SKILL: READING EFFECTIVELY In the space provided, write the letter of the part of the brain that best matches the description. a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. brain stem _____ 1. regulates balance _____ 2. leads to the spinal cord _____ 3. largest part of the brain _____ 4. divided into two hemispheres _____ 5. pons is located here _____ 6. contains the corpus callosum _____ 7. responds to information about body position _____ 8. capacity for learning resides here _____ 9. breathing rate is regulated here _____ 10. located at the base of the brain _____ 11. has a folded layer with many bumps and grooves _____ 12. regulates posture _____ 13. left side controls right side of the body _____ 14. medulla oblongata located here _____ 15. times contractions of the skeletal muscles _____ 16. cerebral cortex is located here _____ 17. located at the posterior base of the brain _____ 18. heart rate is regulated here _____ 19. capacity for intellectual function resides here An analogy is a comparison. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes the analogy. _____ 20. Cerebellum is to movement as cerebrum is to a. breathing. b. walking. c. sleeping. d. perception. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 9 Homeostasis and Human Body Systems






![The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005074380_1-b4c54e7cf592b472b621b12b4eff42cc-150x150.png)