* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Afferents of dopamine neurons
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Substantia nigra wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
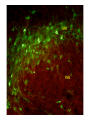
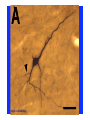
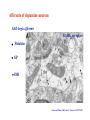
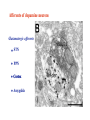
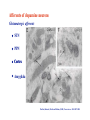
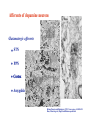
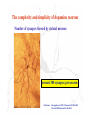
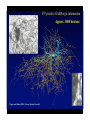
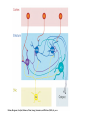
The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons J. Paul Bolam MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit Oxford The normality, complexity, simplicity and subtlety of dopamine neurons J. Paul Bolam MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit Oxford The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Organisation of dopamine neurons at level of SNC (normality) Projections of dopamine neurons (complexity) Responses of dopamine neurons (simplicity) The effects of dopamine neurons (subtlety) Dopamine neurons in SNC DAT immunolabelling SNC SNR TH immunolabelling Dopamine neurons in SNC Bentivoglio and Morelli (2005) Handbook Chem. Neuroanat 21:1-107 Single cell labelling Afferents of dopamine neurons GABAergic afferents Striatum Globus pallidus Substantia nigra reticulata Afferents of dopamine neurons GABA GABAergic afferents TH Striatum Globus pallidus TH Substantia nigra reticulata GAD Afferents of dopamine neurons GABAergic afferents Striatum Globus pallidus Substantia nigra reticulata Fujiyama, Stephenson and Bolam (2002) Eur. J. Neurosci. 15:1961-1975 Afferents of DA neurons GABAergic afferents Striatum Globus pallidus SNR GABA and GABAA receptors Afferents of DA neurons GABAergic afferents Striatum Globus pallidus SNR GABA and GABAA receptors Afferents of dopamine neurons GABAB receptors GABAergic afferents Striatum Globus pallidus Substantia nigra reticulata Boyes and Bolam (2003) Eur. J. Neurosci. 18:3279-3293 Afferents of dopamine neurons GABAergic afferents GABAB receptors Striatum GP SNR Boyes and Bolam (2003) Eur. J. Neurosci. 18:3279-3293 Afferents of dopamine neurons Glutamatergic afferents Subthalamic nucleus Pedunculopontine nucleus Cortex Amygdala Afferents of dopamine neurons Glutamatergic afferents VGLUT 2 STN PPN Cortex Amygdala Afferents of dopamine neurons Glutamatergic afferents STN PPN Cortex Amygdala Chatha, Bernard, Streit and Bolam, (2000) Neuroscience 101:1037-1051. Afferents of dopamine neurons Glutamatergic afferents STN PPN Cortex Amygdala Chatha, Bernard, Streit and Bolam, (2000) Neuroscience 101:1037-1051. Afferents of dopamine neurons Glutamatergic afferents STN PPN Cortex Amygdala Bolam, Francis and Henderson (1991) Neuroscience 41:483-494 Ross, Mena-Segovia, Magill and Bolam unpublished Afferents of dopamine neurons the substantia nigra pars compacta Superior colliculus 5-Hydroxytryptamine: Raphe Noradrenaline: LC Peptides Dopamine Afferents of dopamine neurons the substantia nigra pars compacta SUMMARY Dopamine neurons receive a complex afferent innervation mainly from GABAergic and glutamatergic terminals Ionotropic GABAA and glutamate receptors are mainly located at synapses Metabotropic receptors are located at synapses and extrasynaptic sites GABAergic innervation mainly from St, GP and SNR Glutamatergic innervation mainly from STN and PPN Other functionally important afferents The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Organisation of dopamine neurons at level of SNC (normality) Projections of dopamine neurons (complexity) Responses of dopamine neurons (simplicity) The effects of dopamine neurons (subtlety) Projections of dopamine neurons Striatum GP SNC SNR DAT immunolabelling Projections of dopamine neurons Striatum GP DAT immunolabelling Striatum Globus pallidus The projections of dopamine neurons Topography of the projection medial to lateral/limbic to motor Dorsal and ventral tier Striatonigral projection patch and matrix Based on retrograde and anterograde labelling Bentivoglio and Morelli ( 2005) Handbook Chem. Neuroanat 21:1-107 The projections of dopamine neurons Information flow from frontal cortex through the striatonigral circuit Haber, et al., 2000 J. Neurosci. The projections of dopamine neurons Data from a variety of sources including immunocytochemistry and single cell filling indicate that dopaminergic neurons innervate other regions of basal ganglia GPe Rodrigo et al 1998 Smith & Kieval 2000 Gauthier et al 1999 Prensa & Parent 2001 The projections of dopamine neurons Data from a variety of sources including immunocytochemistry and single cell filling indicate that dopaminergic neurons innervate other regions of basal ganglia GPe Rodrigo et al 1998 Smith & Kieval 2000 Gauthier et al 1999 Prensa & Parent 2001 The projections of dopamine neurons GPe contains DAT-positive axons and boutons Striatum GP Prime, Boyes, Magill and Bolam unpublished The projections of dopamine neurons TH immunolabelling Rodrigo et al 1998; Prime, Boyes, Magill and Bolam unpublished The projections of dopamine neurons STN contains TH-positive and DA-positive axons and boutons Cragg, Baufreton, Xue, Bolam & Bevan 2004 Eur. J. Neurosci. 20:1788-802 The projections of dopamine neurons DA is released from STN upon electrical stimulation Cragg, Baufreton, Xue, Bolam & Bevan 2004 Eur. J. Neurosci. 20:1788-802 The projections of dopamine neurons DA affects the firing of STN neurons Cragg, Baufreton, Xue, Bolam & Bevan 2004 Eur. J. Neurosci. 20:1788-802 The projections of dopamine neurons In addition to innervation of the striatum, dopamine neurons innervate other regions of the basal ganglia Loss of dopamine at the level of the GP and/or the STN may account for some of the changes in Parkinson’s disease Degree of collateralization of individual neurons? Single cell filling studies The projections of dopamine neurons Small deposits of anterograde tracer in SNC Single axons traced to forebrain Characterize the axonal arborization of single neurons Respect patch matrix Prensa and Parent (2001) J Neurosci 21:7247-7260 The projections of dopamine neurons Several classes of neurons based on location and projection Poor respect for the patch/ matrix organisation High degree of collateralization Problems with the technique DA or not size of arborization Based on quantitative anatomical data the arborization of a single dopamine neuron is massive Prensa and Parent (2001) J Neurosci 21:7247-7260 The projections of dopamine neurons Number of synapses formed by dopamine neurons 15000 spines per spiny neuron (Wilson) 4% of spines receive symmetrical synapses (Wilson) Assume half are dopamine terminals and half of dopamine terminals are on spines 7.2 x 103 dopamine neurons in SNC (Oorschott) 2.78 x 106 spiny neurons in striatum(Oorschott) THEREFORE 15000 x 0.02 x 2 x 2.78 x 106 / 7.2 x 103= 231 x 103 synapses per neuron Freund et al 40% spines receive dopamine input which accounts for 60% of terminals THEREFORE 15000 x 0.4 x 2.78 x 106 / 7.2 x 103 +40% = 3.24 x 106 synapses per neuron 369,881 Wickens and Arbuthnott (2005) Handbook Chem. Neuroanat 21:199-236 Neurons of the globus pallidus Kita and Kitai (1994) Brain Res, 636, 308-309 Bevan, Booth, Eaton, and Bolam. (1998) J. Neurosci. 18, 9438-9452 The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Number of synapses formed by globus pallidus neurons Striatum GP SNR SNC EP STN 790 264 or 581 36-209 11-28 approx 100 41-274 Total Max around 1982 synapses per neuron Kita and Kitai (1994) Brain Res, 636:308-309 Bevan, Booth, Eaton, and Bolam. (1998) J. Neurosci. 18: 9438-9452 Sadek, Magill and Bolam unpublished The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Number of synapses formed by striatal neurons around 300 synapses per neuron Data from: Kawaguchi et al 1990 J. Neurosci. 10:3421-3438 Wu et al 2000 Neurosci Res 38:49-62 PV-positive GABAergic interneuron Approx. 5000 boutons Tepper and Bolam (2004 ) Current Opinion Neurobiol. The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Individual dopamine neurons give rise to a massive number of synapses in the striatum Non-synaptic release sites, collaterals to other regions Difficulties of ‘control’ of the whole arborization (branch point failures, local control of release at level of terminals, metabolic support for such a large arborization) Different to other neurons in the basal ganglia The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Juxtacellular labelling of individual dopamine neurons in vivo, chemical characterisation and re-construction Quantitative data on degree of collateralization, numbers of synapses formed and the nature and pattern of innervation of their postsynaptic targets Boyes, Magill and Bolam unpublished Ungless, Magill and Bolam 2004 Science 30:2040-2042 The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Organisation of dopamine neurons at level of SNC (normality) Projections of dopamine neurons (complexity) Responses of dopamine neurons (simplicity) The effects of dopamine neurons (subtlety) Activity of dopamine neurons The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Organisation of dopamine neurons at level of SNC (normality) Projections of dopamine neurons (complexity) Responses of dopamine neurons (simplicity) The effects of dopamine neurons (subtlety) Spiny projection neurons Major target of the nigrostriatal projection Freund, Powell & Smith (1984) The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Major target of dopamine terminals is the spines of MSNs Modulate the flow of cortical information Also innervate striatal interneurons Actions mediated through at least two classes of receptors Smith, Bennett, Bolam, Parent and Sadikot (1994) J. Comp. Neurol. 344:1-19 The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Dopamine receptors located at synaptic and extrasynaptic sites Technical issues relating to receptor immunolabelling Yung, Bolam, Smith, Hersch, Ciliax & Levey (1995). Neuroscience. 65 :709-730 The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Dopamine system is so remarkable because of the plasticity of the corticostriatal synapse Dopamine modulates the flow of cortical information Plasticity of the corticostriatal synapse is often dependent on dopamine Brought about by a variety of mechanisms including LTP, LTD, changes in excitability, receptor interactions, signalling pathways and gene regulation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Figure 4. Effect of dopamine on corticostriatal synapses. Effect of dopamine on activitydependent synaptic plasticity in the corticostriatal pathway. A. A conjunction of cortical presynaptic activity and striatal postsynaptic activity, leads to long-term depression (LTD) in the absence of a dopamine pulse. B. A conjunction of cortical presynaptic activity and striatal postsynaptic activity, leads to long-term potentiation (LTP) if preceded by a dopamine pulse. C. The same conjunction of cortical presynaptic activity and striatal postsynaptic activity, leads to LTD if the dopamine pulse is delayed. Bolam, Bergman, Graybiel, Kimura, Plenz, Seung, Surmeier, and Wickens (2005) In press. The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Dopamine neurons have a complex organisation and afferent input at level of SNC (normality) The projections of dopamine neurons are extremely complex and massive (complexity) Responses of dopamine neurons are relatively simple and uniform (simplicity) The effects of released dopamine at the level of the striatum (other regions of BG/ctx) are subtle and complex and enable dopamine to have profound effects on behaviour (subtlety) The challenge we have set ourselves in DOPANET is to understand one of the most complex neurons in the brain and one of the most complex neurotransmitters The complexity and simplicity of dopamine neurons Thanks to: Peter Magill Yoland Smith Justin Boyes Mark Ungless Fumino Fujiyama Tracey Chatha Hana Ross Juan Mena-Segovia Mark Bevan Stephanie Cragg Bolam, Bergman, Graybiel, Kimura, Plenz, Seung, Surmeier, and Wickens (2005) In press.