* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
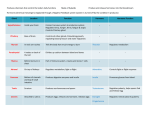
Endocrine System A. Function: Secrete hormones into the circulatory system that will cause a change in the body in a different location Regulated by feedback mechanisms Stimulus-Response Hormones are only released until the appropriate changes are made (homeostasis is restored) B. Structures: 1. Endocrine Glands: Structures/organs that secrete chemicals (hormones) into the circulatory system 2. Hormones: Chemicals that are specific in activity Only work on specific organs/tissues (target cells) Specific in shape Bind with receptor molecules on the out surface of the target cells Effects are slow and long-lasting C. Glands and Hormones Gland Hormone Function & Problems 1. Hypothalamus (brain) (nervous tissue) -controls the pituitary by hormones and nerves 2. Pituitary 1. Growth Hormone (**master gland) -regulates growth (dwarfism, gigantism) 2. Thyroid Stimulating -turns on/off Hormone (TSH) thyroid gland 3. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) 3. Thyroid (throat) Thyroxine - stimulates meiosis in gonads - regulates metabolism - contains iodine (hyper/hypothyroidism, goiter) 4. Parathyroid Parathyroid H. - regulates calcium levels 5. Adrenal 1. Aldosterone (kidneys) 2. - regulates water by controlling blood pressure Epinephrine/ Adrenaline - BP, HR, respir. Fight or Flight 6. Pancreas 3. Norepinephrine - BP, HR, respir. 1. Insulin - blood glucose by storing it in the liver as glycogen 2. Glucagon - blood glucose (DIABETES) 7. Ovary Estrogen 8. Testes Testosterone - FSH estrogen to produce eggs - FSH testosterone to produce sperm