* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins Review - kehsscience.org
Survey
Document related concepts
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
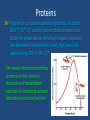
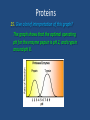
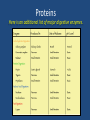
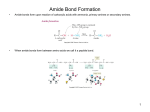
Proteins Review Proteins This structure represents a polymer. 1. What are the individual units called? They are called monomers Proteins 2. What does poly mean? Poly means ‘many’ and polymer means ‘many pieces.’ 3. What does mono mean? Mono means ‘one’ and monomer means ‘one piece.’ Proteins This structure represents a protein. 4. What kind of molecule makes up its monomers? The amino acid Proteins This structure represents a protein. 5. What are the bonds that link the amino acid monomers called? The bonds are peptide linkages Proteins This structure represents a protein. 6. Proteins can be made of one or more strands of amino acids. What is the name given to a single strand of amino acids? Individual strands are called polypeptides Proteins This structure represents a protein. 7. What molecule is released when an amino acid is added to the polypeptide? (Click once to see animation) A water molecule is released Proteins This structure represents a protein. 8. What molecule must be added in order to remove an amino acid from the polypeptide? (Click once to see animation) A water molecule is added Proteins 9. How many different kinds of amino acids are common to living things? There are twenty different kinds Proteins 10. Draw the basic amino acid structure and label its functional groups. H H Amino group N H C O C R Variable group H Carboxyl group Proteins 11. Some amino acids are hydrophilic. What does that mean? It means the amino acids are attracted to water. 12. Some amino acids are hydrophobic. What does that mean? It means the amino acids are repelled by water. Proteins 13. Briefly describe the four levels of protein organization. Example: Spider silk Example: Hair Example: Insulin Example: Hemoglobin Proteins 14. Proteins in our bodies operate efficiently at about 98.6 °F (37 °C), which is normal body temperature. Study the graph below. What will happen to protein function when a person has a very high fever, say approaching 105 °F (41 °C)? The weak interactions holding proteins in their tertiary structure will break down, causing the protein to unravel (denature) and lose function. Proteins 15. Give a brief interpretation of this graph? The graph shows that the optimal operating pH for the enzyme pepsin is pH 2, and trypsin around pH 8. Proteins 16. Trypsin is an enzyme that breaks down proteins in the small intestine. Pepsin also breaks down proteins, however, based on its operating pH, what organ of the body would you expect to find it? Pepsin would most likely be found in the stomach, which has strong acidic juices with a low pH. Proteins 17. List at least four functions of proteins? Act as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions Help transport substances across membranes Store substances the organism needs Help give the cell structure and movement Provides protection against pathogens Helps regulate metabolic processes Proteins 18. List the functions of these common proteins? Amylase: An enzyme that breaks down starches. Hemoglobin: A protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body cells. The main component in hair, nails, and feathers. Keratin: Antibodies: Protects the cell from pathogens. Insulin: A hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Proteins Here is an additional list of major digestive enzymes. Proteins 19. Describe a simple test for detecting proteins in food. a. Put blended samples of the food in a test tube filled with blue Biuret’s reagent. b. Place the test tube in a hot water bath for 3 minutes. If protein is present, the blue color will turn a purple color. Proteins 20. Name some foods that are rich in proteins. Tofu Turkey Fish Cheese Eggs Lean Beef Pork Yogurt & milk Beans Nuts & seeds