* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular Cloning
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
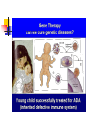
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
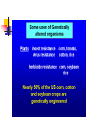
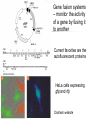
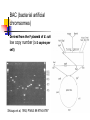
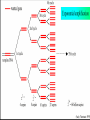
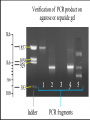
Application in Molecular Cloning David Shiuan Department of Life Science, Institute of Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Program of Bioinformatics National Dong Hwa University Molecular Cloning In order to have enough DNA to work with for a single gene or sequence, you must have a way to “clone”, or reproduce many exact copies of that gene. This is called “molecular cloning” Gene of interest Plasmid Cloning Vector 1. Small 2. Stable in the chosen host – usually E. coli 3. High copy number 4. Easy to purifiy 5. Can accommodate foriegn DNA 6. Single “cloning” sites 7. Selectable marker – antibiotic resistance 8. Easily introduced into host (transformation or transduction Gene fusion systems – monitor the activity of a gene by fusing it to another Current favorites are the autofluorescent proteins HeLa cells expressing gfp and rfp Clontech website YAC(Yeast artificial chromsome) self-replicating vector that can be maintained in yeast Can accommodate large insert Reeves et al., 1992, Methods Enzymol. 216:584-603 BAC (bacterial artificial chromsomes) Derived from the F plasmid of E. coli low copy number (1-2 copies per cell) Shizuya et al, 1992, PNAS 89:9794-8797 Informatics for Molecular Cloning Restriction Enzyme Site Analysis PCR Cloning –primer design Codon Usage Analysis Plasmid Construct – plasmid drawing PCR primer selection Primer Length Melting Temperature (Tm) Specificity Complementary Primer Sequences G/C content and Polypyrimidine (T, C) or polypurine (A, G) stretches 3’-end Sequence Primer 3 Codon Usage – differ from organisms