* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3437 - Allama Iqbal Open University
Survey
Document related concepts
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
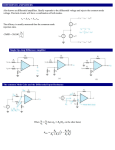
Final: 1-8-2016 ALLAMA IQBAL OPEN UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABA (Department of Physics) WARNING 1. PLAGIARISM OR HIRING OF GHOST WRITER(S) FOR SOLVING THE ASSIGNMENT(S) WILL DEBAR THE STUDENT FROM AWARD OF DEGREE/CERTIFICATE, IF FOUND AT ANY STAGE. 2. SUBMITTING ASSIGNMENT(S) BORROWED OR STOLEN FROM OTHER(S) AS ONE’S OWN WILL BE PENALIZED AS DEFINED IN “AIOU PLAGIARISM POLICY”. Course: Basic Electronics (3437) Level: BS (CS) ASSIGNMENT No. 1 Semester: Autumn 2016 Total Marks: 100 Pass Marks: 50 (Units: 1–5) Note: All questions are compulsory. Each question carries equal marks. Q. 1 What do you understand by P-type and N-type semiconductor materials? Also explain in detail what changes occur after the formation of PN junction. (20) Q. 2 What are bipolar junction transistors? How it works as an AC amplifier? Discuss its all types of amplifying configurations. (20) Q. 3 Write a detailed note on the following: i) Photodiodes ii) Zener diode as Tunnel diodes (20) Q. 4 What is meant by biasing of a BJT? Derive relations for amplifier’s gain, input and output. (20) Q. 5 How PN junction works as rectifier, clipper and clamper? Discuss in detail. (20) ASSIGNMENT No. 2 (Units: 6–9) Total Marks: 100 Pass Marks: 50 Note: All questions are compulsory. Each question carries equal marks. Q. 1 Explain the following: i) Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistor ii) CMOS Q. 2 What are power amplifiers? Also explain transistor power dissipation. (20) (20) Q. 3What do you mean by distortion of Push-Pull amplifiers? How it can be reduced by using feedback? (20) Q. 4 Write a detail introduction of binary, octal and hexadecimal number systems. (20) Q. 5 Discuss in detail Quasi-Class complementary and class C push pull amplifiers. (20) 3437 Basic Electronics Course Code: 3437 Course Title: Basic Electronics Credit Hours: 3 (2 + 1), 2 hours lecture and 3 hours lab per week Session Offered: Recommended Book: As per offering schedule Basic Electronics for Scientists and Engineers by Dennis L. Eggleston (2011) A/V / Multimedia Content: Reference Book: Pre-Requisite: Course Coordinator Teaching Methodology: Computer Usage: As defined by the Instructor / MOOCs links 1. Digital integrated electronics by Herbert Taub and Donald Schilling, Mc. Hraw Hill (1976) 2. University Physics, Freedman. Young. 13th Edition, (2011) None Ch. Muhammad Shahbaz Anjum or Concerned Department Face-to-Face/Online/Blended 3 hours supervised lab per week + about 3 hours unsupervised lab Introduction: This course primarily aims at developing key elementary concepts in basic electronics. The course is designed to explain (Semiconductors, Diode, Transistors, Amplifiers, Logic gates, AC to DC converter, and Binary numbers). Course Objectives: At the end of the course the students are expected to be able to: 1. Know the basic concept of computer. 2. Learn about the function of hardware of the computer. 3. Know the logic of gates functions. 4. Have knowledge of the transistor, diode and amplifiers. 5. Have knowledge of conversion from AC to DC. Evaluation Criteria: i. Assignments and/or quizzes as per instructor’s choice ii. Mid Term Theory/practical /presentation/mini projects as per instructor’s choice 20% iii. Final Examination 70% 2 10% Course Outline: Unit# 1: Semiconductor Semiconductor materials, P and N Types, PN junction, forward and reversed biased junctions, PN junctions as a rectifier, clipper and clamper circuits Unit# 2: Diodes Zenor diode, Zenor breakdown, Zenor voltage regulator LCD, LED, Photo diodes, Tunnel diodes, Operation of the junction diodes. Unit# 3: Transistors Introduction to Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), Theory of BJT operation transistor, types and need, purpose of basing transistor types, BJT AC amplifiers fundamentals, Amplifiers gain, input and output. Unit# 4: Metal Oxide Transistors Metal Oxide transistors, Depletion type, Metal oxide field effect transistor, nMOS, pMOS and CMOS. Unit# 5: Power Amplifiers Basic considerations, Heat transfer in semiconductor devices, Transistor power dissipation. Unit# 6: Amplifier Classes Push-pull amplifiers, use of feedback to reduce distortion, Distortion in push-pull amplifiers, Quasi-class complementary push-pull amplifiers, Class C amplifiers Unit# 7: Binary System Conversion of binary numbers in octal and hexadecimal. Binary codes and logic. Unit# 8: Power Control Circuits Introduction and concept of AC to DC and DC to AC converters Activities / Practical: 1. Construction of half wave, full wave, bridge rectifier circuits 2. Capacitor filter, Introduction filter, Pi section filter. 3. Construction of Zener voltage regulator. 4. Construction of discrete component logic gates (OR, AND, NAND, NOT). Note: The instructor may assign additional activities. Last revised: June 2015 3