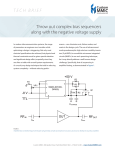
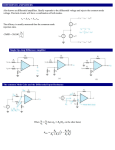
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ET161 - Mohawk Valley Community College
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
MOHAWK VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE UTICA AND ROME, NEW YORK CENTER FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS COURSE OUTLINE I. CATALOG DESCRIPTION: ET161 Linear Electronics C-2, P-2, CR-3 The theory and applications of modern transistors are introduced; both the bipolar junction transistor and the field effect transistor are examined. Applications include usage in small and large signal class A amplifiers, as well as in class B power amplifiers. Voltage control FET applications are studied. Problem solving techniques involving digital computers are discussed. II. III. Prerequisites: ET153 Introduction to Electronics, ET154 Computer Programming, or permission of instructor. Corequisites: ET152 Circuits 2 or permission of instructor. MATERIALS: Text: Electronic Principles, 7th edition, ISBN #0073222776, by Malvino, McGraw-Hill Publishing Lab Manual: Laboratory Manual for Linear Electronics, by Fiore. Available on-line at www.mvcc.edu/jfiore and at open educational resource sites Tools: Scientific calculator, electronic hand tools and breadboard STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES: The student will demonstrate familiarity with the operating principles and linear applications of bipolar and field effect transistors. (a) The student will demonstrate a working knowledge of the basic theory of device operation, how to properly bias devices, and have an understanding of common circuit applications including small and large signal audio amplifiers. (a) The student will use a mathematical and problem solving approach for design and analysis, based on fundamental DC and AC circuit principles and math concepts. This will include the use of computer simulations. The student will demonstrate facility at constructing and trouble shooting transistor circuits in the laboratory with proper use of test equipment. (c) The student will demonstrate appropriate communication skills, particularly technical reports through the laboratory. (f) The student will demonstrate the ability to work as part of a technical team, particularly in the laboratory. (d) () – References ETAC of ABET Program Outcome 1 IV. DETAILED COURSE OUTLINE: 1. Bipolar Transistors: Structure and Biasing A. Basic construction and theory B. Forward-reverse bias 1. Alpha 2. Breakdown C. Common Emitter Connection 1. Equivalent circuits 2. Current gain (beta) D. Device Characteristics 1. Base curves 2. Collector curves 3. Maximum and typical ratings E. DC Load Line F. Transistor Current Source and Switch G. Bias Forms: Operation and Stability 1. Base bias 2. Two supply emitter bias 3. Voltage divider bias H. PNP Circuits 2. Small Signal Amplifiers A. CE Amplifiers 1. Capacitors, AC models and Superposition 2. r’e 3. Voltage gain, input and output impedance 4. Cascaded stages B. CC Amplifiers 1. The voltage follower: gain, impedances, etc. 2. Darlington pair 3. Large Signal Amplifiers A. Amplifier classification B. Class A 1. AC load line 2. Gain and power 3. Distortion and C. Class B 1. AC load line 2. Gain and power 3. Distortion and D. Device Power Ratings calculations efficiency calculations efficiency 4. Field Effect Transistors A. Junction FETs 1. Theory of operation, comparison to bipolars 2. Biasing techniques and models 3. Common source: gain, impedances, etc. 4. Common drain and gate: gain, impedances, etc. B. MOSFETs 1. Depletion-enhancement type: differences to JFET 2. Enhancement only type: differences to DE-MOS 3. Power FETs 2 V. LABORATORY OUTLINE: Students should submit technical reports for the laboratory exercises. Appropriate graphs, tables, and subsequent analysis are expected along with proper spelling and grammar. Laboratory results may also be verified through computer simulations. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Diode Curves Base Bias LED Drivers Voltage Divider Bias Emitter Bias Feedback Biasing PNP Transistors Common Emitter Amplifier Swamped Amplifier Voltage Follower Class A Power Analysis Class B Power Analysis Power Amp with Driver JFET Bias JFET Amplifiers Alternates: The Zener Diode In addition to the laboratory exercises, the student may be required to write a short research paper using the library facilities. Appropriate topics include (but are not limited to) items such as: Investigation of distortion causes, present state of the art for transistor speed or power parameters, comparison of bipolar and field effect devices in certain application areas, a comparison of modern amplifier designs to those of 20 years ago, how to model dynamic loudspeakers, theory of moving coil dynamic microphones, public address system design, etc. A short presentation would be in order for the final lab period. VI. POSSIBLE PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENTS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. DC Analysis of Bipolar Bias Configurations AC Analysis of Bipolar Small Signal Amplifiers FET Circuit Analysis Analysis of Class A or B Power Amplifiers Load Line Verification 3 COURSE NAME: ET161 Linear Electronics DATE FACULTY NAME 08.23.06 Fiore 11.22.06 Fiore 05.21.07 Fiore 05.25.12 Fiore 09.12.13 Fiore 09.10.14 Fiore 11.25.14 Fiore 09.14.15 Fiore CHANGE _________________ INPUT MEASUREMENT ASSESSMENT ACTION Updated Learning Outcomes and changed lab #s to conform to 7th Ed. Updated Catalog Description, stylistic consistency Student performance Via course rubric: lab performance, reports, and tests All students passing course reached satisfactory assessment targets None Required Updated lab exercise sequence Updated for new lab manual Periodic review Added references to ETAC of ABET Program Outcomes Updated for reduction to 3 credit hours from 4 SUNY-Stated Ed requirement for 64 program hours 1