* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Antique radio wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
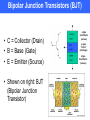
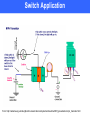
Introduction to Transistors Instrument Systems Spring 2007 Jose Rey April 2007 Transistors • Everywhere • Similar diodes end-to-end (np-n and p-n-p junctions • Sandwiched junction is very thin • Small current on the “base” can control a large current flowing from “collector” to “emitter” • Can be used as an amplifier to make a weak signal stronger • Can replace mechanical switches Transistors • First Transistor • Bell Labs • First transistor was point contact Ge bipolar junction transistor Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) • C = Collector (Drain) • B = Base (Gate) • E = Emitter (Source) • Shown on right: BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) n-type Contributor (excess) p-type “holes” (shortage) n-type Contributor (excess) Switch Application From: http://natasha.eng.usf.edu/gilbert/courses/instrumentsystems/showtime/2005_presentations/npn_transistor.html Field effect transistor (FET) • Only two layers • Electric Field Controls Current Flow • Voltage applied between the Gate and Source terminals modulates the current between the Source and Drain terminals • Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) or junction field effect transistor(JFET) • Large amount of Chemical Sensors are based on MOSFETs C = Collector (Drain) B= Base or Gate E = Emitter (Source) Diodes Quick Review • Diodes AND LED’s Current flows from Anode+ to Cathode• Place a LED in the following circuit, how? Transistors Quick Review • In NPN Transistor Collector AND Emitter are n doped, Base is p doped • When Transistor is saturated, current flows at maximum AND no longer controlled by Base End of presentation