* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Visual search wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Process tracing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Visual servoing wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Visual memory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Efficient coding hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
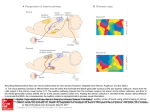
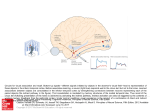
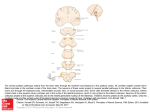
Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the primary visual cortex to areas in the parietal lobe (the dorsal pathway, which is concerned with visually guided movement) and areas in the temporal lobe (the ventral pathway, which is concerned with object recognition). The pulvinar also serves as a relay between cortical areas to supplement their direct connections. B. Pupillary Source: reflex and Light are relayedPrinciples through the midbrain pretectum, to preganglionic parasympathetic neurons in the Theaccommodation. Constructive Nature of signals Visual Processing, of Neural Science, Fifth Editon Edinger-Westphal nucleus, and out through the parasympathetic outflow of the oculomotor nerve to the ciliary ganglion. Postganglionic neurons innervate Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available the smooth muscle of the pupillary sphincter, as well as the muscles controlling the lens. at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 02, 2017 C. Eye movement. Information from the retina is sent toAllthe superior colliculus (SC) directly along the optic nerve and indirectly through the geniculostriate Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. rights reserved pathway to cortical areas (primary visual cortex, posterior parietal cortex, and frontal eye fields) that project back to the superior colliculus. The colliculus