* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Inferior temporal gyrus wikipedia , lookup
Superior colliculus wikipedia , lookup
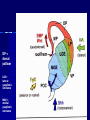
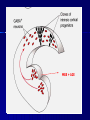
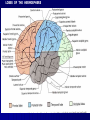
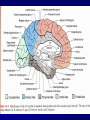
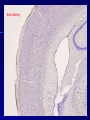
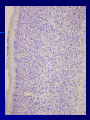
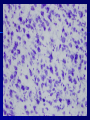
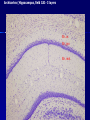
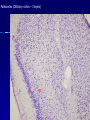
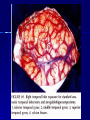
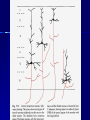
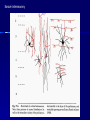
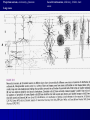
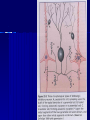
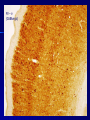
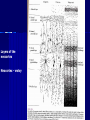
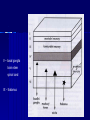
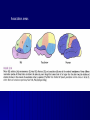
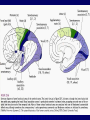
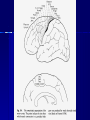
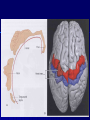
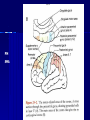
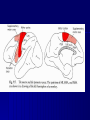
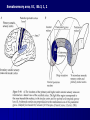
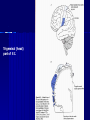
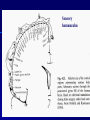
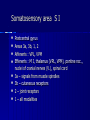
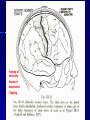
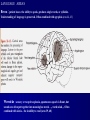
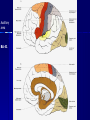
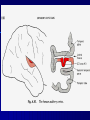
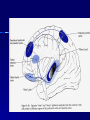
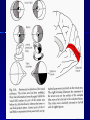
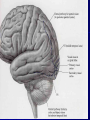
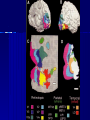
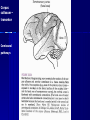
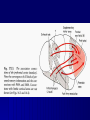
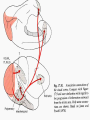
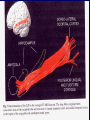
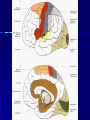
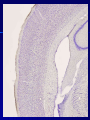
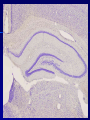
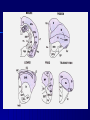
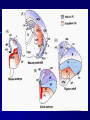
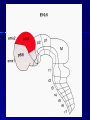
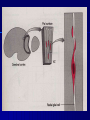
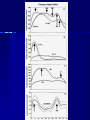
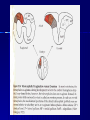
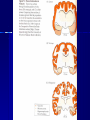
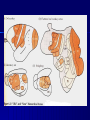
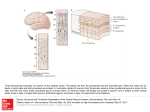
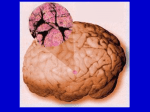
THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Institute of Anatomy, 1st Medical Faculty R. Druga CORTEX CEREBRI Definice, Definition Neocortex, Allocortex Vývoj hemisféry a neokortexu Development of the neocortex Struktura neokortexu Structure of the neocortex Hlavní typy neuronů Main types of neurons DP = dorsal pallium LGE= lateral ganglionic eminence MGE = medial ganglionic eminence MGE + LGE NEOCORTEX Laminar pattern – 6 layers 10 – 20 billion neurons 95 % surface of the hemisphere LOBES OF THE HERMISPHERE Nissl staining Archicortex (Hippocampus, field CA1- 3 layers Str. or. Str, pyr. Str. mol. Paleocortex (Olfactory cortex – 3 layers) I. II, III. Astrocyty (imunoreaction GFAP) NEOCORTEX, types of neurons Pyramidal neurons Non-pyramidal neurons Apical and basal dendrites Dendritic spines Excitatory (glutamate) Homogenous group 60 – 70 % Aspiny Heterogenous group Inhibitory (GABA) 30 – 40 % Pyramidal neurons Layer V. MI Golgi impregnation Korové interneurony Projection neurons, excitatatory, glutamate Long axons Local circuit neurons, inhibitory, GABA, short axons PV – ir (GABAergic) CALRETININ – IR (GABAergic) My investigations showed that the functional superiority of the human brain is intimately bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. S. R. y Cajal: Recuerdos de mi vida. 1917. Interneurons are butterflies of the soul. S.R. y Cajal 1923 Petilla de Aragon (Cajal birthplace) 2005 „Petilla Convention“ K.Brodmann, 1907, 1911 11 regions 52 areas Layers of the neocortex Neocortex - vrstvy Characteristics of layers I.. Molecular layer – local inhibitory interneurons II. External granular – association neurons III. External pyramidal – commissural neurons IV. Internal granular – receives thalamocortical projections V. Internal pyramidal – projecting neurons (basal ganglia, brain stem, spinal cord VI. Multiform layer – corticothalamic neurons V – basal ganglia brain stem spinal cord VI - thalamus Excitatory connections in the neocortex Layer 4 – termination of thalamocortical projections Layer 4 – projects to layer 3 Layer 3 – projects to layer 5 Association areas Afferent neocortical connections Thalamic nuclei (thalamocortical fibers) Amygdala Claustrum Hypothalamus Nc. basalis (Meynert)-cholinergic system Raphe nuclei (serotonin) Locus coeruleus (noradrenalin) Subst. Nigra (VTA) - dopamin Efferent neocortical connections (excitatory, glutamatergic) Thalamic nuclei Basal ganglia (striatum, amygdala, claustrum) Brain stem (pretectal area, tectum, nc. ruber, RF, nuclei of cranial nerves, pontine ncc., nc. gracilis, nc. cuneatus) Spinal cord ( corticospinal pathway, interneurons, motoneurons) Motor cortical area G. Fritsch and E. Hitzig (1870) demonstrated that electrical stimulation of the dog´s frontal lobe results in contralateral muscular contractions (movements) Primary motor area, MI Motor homunculus Primary motor area M I Precentral gyrus, area 4 Part of the cortex from which movements are easily produced by electrical stimulation Motor homunculus (overrepresentation muscles of the thumb, hand, face, tongue, distorted somatotopic representation) Afferents : S I, thalamic VL (cerebellum) Efferents : basal ganglia, thalamus, (VL) RF, superior colliculus, nc. ruber, RF, pontine ncc., spinal cord Control of distal muscles Damage produces paralysis of contralateral muscles (namely upper limb, tongue, facial muscles) THE CORTICOSPINAL PATHWAY PM SMA Premotor area, PM Area 6 Somatotopic representation of the body musculature, less precisely organized Efferents – M I, basal ganglia, RF, Spinal cord (influences paravertebral and proximal limb musculature) Afferents – thalamic VA (basal ganglia), S I, Preparation to move Supplementary motor area Area 6, medial surface of the hemisphere Somatotopic organization,less precisely organized Afferents – thalamic VA (basal ganglia), parietal cortex Efferents – MI, Basal ganglia, RF, Spinal cord Area is involved in organizing and planning the sequence of muscle activation Somatosensory area, S I, BA 3, 1, 2 Trigeminal (head) part of S I. Sensory homunculus Somatosensory area S I Postcentral gyrus Areas 3a, 3b, 1, 2 Afferents : VPL, VPM Efferents : M I, thalamus (VPL, VPM), pontine ncc., nuclei of cranial nerves (V.), spinal cord 3a – signals from muscle spindles 3b – cutaneous receptors 2 – joint receptors 1 – all modalities Feeling of elictricity Sense of movement Tingling Homunculus Distribution of signals from primary sensory area – to close associative area and finally to distant polysensory areas and to limbic cortex (memory, emotions) LANGUAGE AREAS Broca : patient losses the ability to speak, produces single words, or syllables. Understanding of language is preserved. Often combined with agraphia (area 44, 45) Wernicke : sensory or receptive aphasia, spontaneous speech is fluent, but sounds are often put together into meaningless words – „ word salad „. Often combined with alexia – the inability to read (area 39, 40) Auditory area BA 41 Auditory area Superior temporal gyrus (gyrus temporalis transversus, Heschl gyrus) Area 41 = primary auditory area (A I) Areas 42, 21, 22 = associated auditory areas (A II) Afferent connections from auditory pathway (cochlear ganglion – cochlear nuclei- superior olive – inferior colliculus – medial geniculate body – BA 41) Efferent connections ( A I – A II – temporal, parietal, frontal lobe, Broca area) Auditory cortex Area 41 Afferents – auditory pathway (thalamic medial geniculate body) Efferents – thalamus (medial geniculate body), inferior colliculus, associative cortical areas (what and where paths) Visual cortex Area 17, granular cortex Afferents – visual pathway, thalamic lateral geniculate body. Overrepresentation of central part of retina. Efferents – thalamus (lateral geniculate body), area 18, 19, parietal cortex, temporal cortex. Dorsal stream – parietal cortex (where : rods, periphery of retina, area 7) Ventral stream – temporal cortex (whatcolors, form, surface : cones, central area of retina, area 37, inferior. temporal cortex Receptor mapping Receptor concentration fmol/mg protein (K. Zilles et al. 2010) Cortical commissural pathways Corpus callosum (250 – 300 millions fibers, originate in layer III, mainly excitatory Anterior commissure – pars olfactoria, pars interhemispherica Commisura fornicis (hippocampi) Corpus callosum – transekce Comissural pathways Associative pathways Short pathways – interconnect close cortical areas ( area 6 with area 4) Long pathways – interconnect distal cortical areas or lobes (occipital with frontal) Cerebral cortex All mammals depend on it. A man without a cortex is almost vegetable, speechless, sightless, senseless (D. Hubel and T. Wiesel 1979). The cortex supports sensory perception, reasoning, planning and execution of behaviors. Thank you ! Neocortex - definice 6 vrstev, 6 layers 10 – 20 miliard (bilions) neuronů 95 % povrchu hemisféry 95 % of the hemisphere surface CALRETININ - IR PV– ir, V - VI ÚPRAVA HEMISFÉRY Hemisféra – evertovaná Hemisféra - evaginovaná