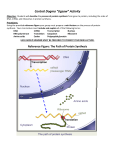
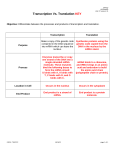
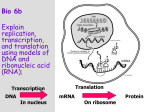
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis Notes - Hamilton Local Schools
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein Synthesis Notes DNA to proteins Connections: • Know where each stage of protein synthesis occurs in the cell. • Given a sequence of DNA construct the protein using transcription and translation. • Understand and demonstrate how start and stop codons effect the synthesis of a protein. Review • One of the functions of proteins is to __________________ cellular processes, such as ______________________ and cellular ________________. • DNA are the instructions for _________________. • Proteins are made up of __________________________. DNA tells the body the amino __________________ to create specific proteins. What is Protein Synthesis? • Protein synthesis is the process of making ______________________ from ____________. • It has _______ stages o ______________________________ o ______________________________ Protein Synthesis • Transcription: _________ is made from __________ • mRNA leaves the __________________ and goes to the ________________________. o Why make mRNA? o ________________________________________________________________________ • Translation: Ribosomes “read” the mRNA code and create a __________________ by bonding individual ____________ __________ together. ________________ • ________________ _______ → → → → → → → → _________ → → → → → → → → ____________ mRNA vs DNA • mRNA is a copy of the _________ that can ___________ the nucleus. • mRNA is a ________________________ and made of _______________________. • mRNA is: o The sugar ____________ instead of deoxyribose o It is ________________________________ o It has _____________ instead of _______________. Transcription • Transcription happens in the ___________________. • It is where _________ is made from the _________ strand. • Only _______ side of the DNA strand is used. o This is called the ____________ strand. Transcription Example • Given the following coding DNA strand perform transcription. o C T T A G A G G C o ______________________________________ Transcription Example • Given the following mRNA strand perform reverse transcription. ◦ A U G C G A U C A ◦ ________________________ Transcription Practice Perform transcription on the DNA template: 1. C A G A G C C T G T ________________________________________ 2. C T T C T G T G C A ________________________________________ Perform reverse transcription on the mRNA sequence 3. C G G A G U G C A U U ________________________________________ Translation • Translation happens in the ______________________. • Translation: The _______________ of an __________ message into a ______________. o Protein is a long chain of bonded ____________ ___________. o The mRNA tells the ribosome what the sequence of amino acids is for that protein. • During translation, the cell uses information from messenger RNA (mRNA) to produce _____________. How does the ribosome “read” mRNA? • The “language” of mRNA instructions is called the ______________ _________. • All living organisms use the ___________ same __________ nucleotides for their DNA. o A sequence of fish DNA can be read just like a sequence of human DNA. • mRNA is made up of _____, ______, ______, and _______. • Notice there are no ______ in mRNA. The Genetic Code • The genetic code is read ___________ letters at a time. o So, each “word” in mRNA is known as a ____________. • So, each “word” in mRNA is known as a _____________. • Codon: ___________ consecutive _______________________ that specify a ____________ amino acid that is to be added to the protein. o Example: ____________ • The amino acids that each ____________ codes for can be found using the genetic code table. o All codons code for the ____________ same amino acid in _____ living organisms. The Genetic Code Table Translation • Consider the following mRNA sequence: _________________________________ • This sequence would be read three bases at a time as: _________________________________ • The codons represent the different amino acids: _________________________________________________________ Translation Problem • mRNA sequence: AUG CGU ACC UUA CAG GGG • Amino Acid Sequence: _____________ - ____________ - ____________ - _____________- ____________ - _____________ Translation Problem • Write a possible mRNA sequence for following protein: Isoleucine (Ile) - Alanine (Ala) - Tyrosine (Tyr)- Leucine (Leu) • Possible mRNA sequence: ________ - ________ - ________ - ________ Start Codon • The ribosome will ______ start to construct a protein until it reads a certain mRNA sequence called the _____________ ____________. • The start codon is: _________ which always codes for _______________________ (_______) Stop Codons • The ribosome ___________ constructing the protein when it reaches a _________ ___________. • The stop codons are: _________, __________, and ___________ Protein Synthesis Problems 1. What is the protein constructed from the following strand of DNA: TAC GGA TTC AGA • Step 1: Transcription ________ - ________ - _________ - _________ • Step 2: Translation _______________ - _______________ - _______________ - _______________ 2. What is the protein constructed from the following strand of DNA: CCG TAC GGA TTC ACT AGA • Step 1: Transcription ________ - ________ - ________ - ________ - _________ - _________ • Step 2: Translation _____________ - _____________ - _____________ - _____________ - ______________ _____________ Start Codon Continued • The _______________ reads the mRNA until it finds a __________ codon sequence. • The start codon may be _____________ among the mRNA. The ribosome will read through until it finds it. Find the Start Codon • Here is an mRNA sequence. Find where the protein starts to be made and circle it CGGUAUGACUCCCUAACA • Perform translation on the sequence • What is the DNA sequence that made this mRNA?