* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transparency master
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
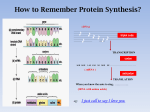
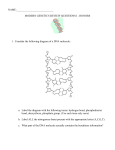
Transparency master – vocabulary Anti-codon – a group of 3 nucleotides in tRNA that complements the codons on the mRNA Codon - a group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid Transcription – process by which mRNA molecules are copied from the DNA Translation – when codons in mRNA are decoded into a sequence of amino acids DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid, double-stranded helix that carries all genetic information available is every cell mRNA – single-stranded messenger that carries copies of DNA segments to the ribosome where proteins are made, contains uracil instead of thymine tRNA – transfer one amino acid after another to the ribosome, contains uracil instead of thymine ribosome – contains ribosomal RNA that are used to assemble proteins nucleus – control center of the cell, where the DNA is “trapped” by the semi-permeable nuclear membrane