* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
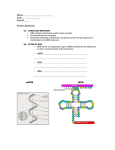
Lecture 4 Transcription Dr. M. A. Fouad Gene Expression Protein synthesis involves two processes: transcription and translation. In transcription the DNA message is converted into an mRNA molecule. In translation the mRNA message is used to assemble amino acids into a protein chain. Transcription: Definition gene • Transcription: Is the process in which genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA. DNA (nucleus) Transcription • Transcription: is the process of synthesis a single strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) with the same sequence as the original DNA strand. • Transcription is the first step of gene expression messenger RNA (cytoplasm) Transcription: RNA Polymerase Enzyme • Transcription is catalyzed by the enzyme RNA polymerase. • RNA polymerase catalyzes the synthesis of RNA on a DNA template strand. Transcription: The template strand • In any particular gene only one DNA strand of the double helix acts as (template strand). • The transcribed mRNA is a copy of the complementary strand (the sense strand) of the DNA double helix. • The template strand is sometimes called the antisense strand. Sense strand (Anti-sense strand) Sense strand (Anti-sense strand) The transcription Process • RNA polymerase recognizes the start of a gene (promoter) and unwinds a segment of it. start site transcription complex nucleotides The Transcription Process • RNA polymerase begins moving down the DNA template strand in the 3' to 5' direction. • As it does so, it synthesize complementary mRNA in the 5' to 3' direction. – Once the gene is transcribed, the RNA strand is released and RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA. RNA Complementary RNA pairs • The base-pairing during transcription is the same as when DNA replicates, except that RNA has uracil instead of thymine: the base U in RNA pairs with A in DNA. . RNA DNA Complementary RNA pairs Template Strand Quizzes 1. The enzyme required for transcription is A. B. C. D. Ligase DNA polymerase RNA polymerase RNAase 2. The process involved in the mRNA formation on the DNA template is: a) b) c) d) Transcription Translation Replication Transformation 3. Which is found in RNA but not in DNA? A. B. C. D. E. Adenine Cytosine Guanine Uracil phosphate groups 4. Transcription is the transfer of genetic information from A. B. C. D. DNA to rRNA tRNA to mRNA DNA to mRNA mRNA to tRNA 5. The DNA chain acting as template for RNA synthesis has the following order of bases, AGCTTCGA. What will be the order of bases in mRNA? A. B. C. D. TCGAAGCT UGCUAGCT TCGAUCGU UCGAAGCU RNA Processing Post-transcription modification • The transcription results initially in a premessenger RNA (pre-mRNA) molecule. • pre-mRNA must undergoes a number of modifications, or what is known as “RNA processing”, before it leaves the nucleus. RNA processing Post-transcription modification include 1. mRNA splicing 2. 5’ capping 3. 3’ Polyadenylation 1- mRNA splicing • Most eukaryotic protein-coding genes contain non-coding segments called introns, which break up the coding sequence into segments called exons. • The coding regions of the RNA transcript are called exons. 1- mRNA splicing Splicing is an RNA-processing step in which: • The Introns (non-coding sequences) are removed. • The exons (coding sequences) are re-joined again. RNA Splicing 2- RNA processing 5’capping • A cap structure is added to the 5’ end of the transcribed RNA. • 5’ capping: is the process of adding methylated guanine nucleotide to the 5’ end of the RNA molecule by an unusual 5 ' to 5' phosphodiester bond. Cap structure at the 5 end of a eukaryotic mRNA RNA processing 5’capping 5’ capping process in important because: • Facilitate the transport of mRNA from nucleus to the cytoplasm. • Facilitate the attachment of mRNA to the ribosome. • Protect mRNA from degradation by endogenous cellular exonuclease. RNA processing-Polyadenylation • Polyadenylation is the process of adding 200 adenylate molecules to the 3’ end of mRNA to form what is called as poly(A) tail. • This process is important for the transport of RNA from nucleus to cytoplasm and translation. Mature mRNA structure Quizzes 6. The process of removing introns and joining exons is known as: A. B. C. D. mRNA splicing 5’ capping Polyadenylation Transcription 7. What is added to the 3'-end mRNAs during mRNA processing? A. Introns B. Poly A tail C. A cap structure, consisting of a methylated G nucleotide D. Exons 8. The non-coding segments that are removed during mRNA processing are called? A. B. C. D. Introns Exons Codons Anticodon 9. What is added to the 5'-end mRNAs during mRNA processing? A. Introns B. a poly A tail C. a cap structure, consisting of a methylated G nucleotide D. exons