* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning? What`s that?
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
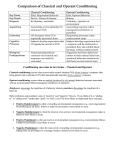
Learning? What’s that? • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A ‘relatively’ permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice. Note that learning is NOT the same as maturation (like walking or toilet training). Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Cognitive Learning Latent Learning Observational Learning Classical Conditioning? Pavlov’s name ring a bell? • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. Learning by association, we perform a reflex or involuntary behavior to a new stimulus. We need a UCS and UCR, and then we add a CS and eventually we get a CR. Huh? Some essential criteria CS must precede UCS in acquisition phase CS and UCS pairing is time sensitive 1 or 2 pairings will usually not be enough CS needs to be distinctive Anything else I ought to know about CC? • • • • • Stimulus generalization: responding to a stimulus that’s similar to the CS Stimulus discrimination: spotting how a stimulus is different from the CS Extinction: what happens with no UCS? Spontaneous Recovery: hey, there’s still something left after extinction? Higher Order Conditioning: using a pairing of an NS with a CS, and after a while we’ve got a new CS. Are there other forms of CC? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Conditioned Emotional Response: Poor lil’ Abert… so afraid of a harmless white rat. Vicarious Conditioning: all I gotta do is notice how somebody else responds to the CS? Conditioned Taste Aversion: Why Neil isn’t a tequila fan? Note 1 trial learning. Bio prepared! Theories and explanations? You betcha! Pavlov says process is stimulus substitution. Cognitive psychologists believe there must be an expectancy created by the CS/UCS pair. Operant Conditioning? What’s that? Thorndike’s cats in boxes helps him establish the “Law of Effect”. Skinner continues the trend with rats in boxes. • What do we mean by a reinforcer? • Some reinforcers are primary? • Some reinforcers are secondary? • How are they different from a punisher? • Both things can be either positive or negative? Huh? What sorts of things effect how quickly or long lasting operant learning works? • • • • Continuous reinforcement. Simple and fast Partial reinforcement. Slower but steady Fixed intervals work pretty well for work. Variable intervals work against gamblers Anything else important to consider? 1. 2. Speed matters (like with CC), but now we need a speedy delivery of the reinforcer. We need to make sure we are reinforcing the correct response ONLY! Enough about Reinforcement. What about Punishment? • 1. 2. 3. • • Punishment reduces the likelihood that a response gets repeated. May be + or It works best if it is intense or severe (uh oh) It needs to be consistent (creates gambling) Even when it works, results often temporary It may create fear, avoidance, anxiety, lying and/or animosity It teaches violence (if we believe in modeling) and messes up my relationships Anything else about Operant Conditioning? • • • • • A Discriminative Stimulus works as a cue to direct us toward certain behavior (cops!) Behavior Modification allows us to target certain behaviors (to increase or decrease) Shaping allows us to gradually teach someone a very complex behavior (chain?) Token economies allow us to skimp on reinforcers Some behavior is biologically constrained What about THINKING?!? • • • • • • Cognitive Theorists focus on mental processes Tolman discovers rats show latent learning and develop cognitive maps Kohler discovers that chimps use insight to problem solve Seligman discovers that dogs can learn helplessness and mimic depression Humans can learn to control HR, BP, GSR and peripheral vascular using Biofeedback… and Specific Brain activity or patterns using Neurofeedback Any other learning stuff happenin’? • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. Bandura discovers that kids go beyond vicarious conditioning to modeling the behavior of others… sometimes. Do we need to worry about violent video games? Four Keys to Observational Learning Attention: must notice the model’s behavior Memory: must store & retrieve information Imitation: must be able to do the behavior Motivation: no desire… no luck