* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. Purification of WDR77
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
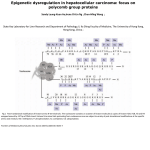
ABSTRACT The WD40 repeat domain protein, WDR77 Post-translational modification of histone tails is one of the primary modes of epigenetic regulation. The multiple types of post-translational modifications include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitylation, sumoylation, ADP-ribosylation, proline isomerization, citrullination, butyrylation, propionylation and glycosylation. Methylation of arginine residues in histone tails is a predominant type of modification and the marked feature of this modification is that different methylated states i.e. monomethylated or dimethylated can direct different transcriptional consequences. Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) are a group of enzymes that attach a methyl group to a guanidino nitrogen atom of arginine using S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) as the source of the methyl group. PRMT5 has been shown to have an intracellular dependence on the interacting WD40 repeat domain -containing protein WDR77 to determine specific substrates. Furthermore, the WD40 domain containing protein WDR77 has been shown to interact specifically with histone H2A. However, the dependence of the interaction between WDR77 and modified histone H2A has not been clarified. Some evidence suggests that H2AR3 methylation occurs in the cytosol and is deposited into nucleosomes by chaperones as a dimer with H2B, suggesting a sophisticated mechanism of nucleosome assembly and remodeling to ensure proper installation of H2AR3me2 throughout the genome. Furthermore, the role between PRMT5 and WDR77 to identify specific substrates remains unclear. In this study we begin to determine the criteria for WDR77 recognition of specific substrates for PRMT5 and to determine the functions of both cytosolic and nuclear isoforms of the WDR77/PRMT5 heterodimeric complex to enact specific genomic regulatory functions with H2AR3me2 methylation. Results WD repeat containing protein 77 (WDR77) is a 342 aa WD repeat protein that is present in the nucleus and cytoplasm. It has seven putative WD domains, three Nuclear Localization Sequences (NLS) and two Nuclear Exclusion Sequences (NES). It has been separately reported as MEP50 (Methylosome protein 50) and p44 (co-factor of androgen receptor). Cytoplasm 1. Peptide pull down assay Nuclear Extract – PC3 nuclear extract Peptides used 1. No peptide – C 2. Unmethylated H3R2 peptide- UN 3. Assymmetrically dimethylated H3R2 peptide – 2A 4. Symmetrically dimethylated H3R2 peptide – 2S 20S Methylosome pICln Nuclear membrane WDR77 Sm proteins WDR77 Heat denatured fractions UN C Me PRMT5 PRMT5 Acid elution fractions H2A C 2A 2S UN 2A 2S Nuclear Pore complex M WDR5 Sm proteins Nucleus H2AR3me2s M WDR77 H2AR3me2s/ H2B dimer PRMT7 Figure 4 - WDR77 interactions in the cytoplasm. WDR77/MEP50 is a part of the 20S methylosome complex. PRMT5/WDR77 complex catalyze the symmetric dimethylation of H2AR3 and this is essential for stem cell maintenance. Figure is not drawn to scale. 2. Purification of WDR77 M FT W E E E2 FT W E E2 250 150 100 75 PRMT5 50 P CycD1 WDR77 37 SUZ12 WDR77 WDR77 Transcription FCP1 WDR77 NuRD complex PRMT5 PRC-2 complex PRMT7 MBD2 WDR77 M-Marker FT- Flow through fraction W-Wash fraction E and E2- Elution fractions 25 WDR77 AR/ER Densely packed heterochromatin Conclusion mRNA P Figure 1- Organization of the nucleosomal histone NH terminus (Fullgrabe 30:3391-3403). et. al. (2011) Oncogene Figure 2- Distinction between assymmetrical and symmetrical arginine dimethylation by protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) (Di Lorenzo A. and Bedford M.T. (2011) FEBS Letters 585(13):2024-31) Figure 5- WDR77 interactions in the nucleus. WDR77 interacts with proteins in the actively transcribing as well as repressed regions of the genome. AR/ER-androgen receptor or estrogen receptor, Cyc D1- Cyclin D1. Figure is not drawn to scale. WD40 proteins Among the many protein domains that recognize histone modifications, the group of WD repeat proteins constitute a large heterogenous family of proteins. The WD repeat proteins get their name by carrying repeats of amino acid residues within a stretch of 40-60 amino acids that begin with a Glycine-Histidine (GH) dipeptide and end in a Tryptophan-Aspartic acid dipeptide (WD). WD repeat generally contain 7 repeats that are arranged in a circular manner forming a β propeller structure (Figure 1). This structure enables WD repeat domains to act as a scaffold to accommodate the interaction and assembly with a diverse array of proteins and their structures. Phosphate group Methyl CpG Although the peptide pull down assay showed WDR77 interaction with the H3R2Me2s and H3R2Me2a peptides it remains to be confirmed if there is direct binding. The assay should be repeated using the purified WDR77 protein. Future experiments also include ChIP assays to determine WDR77 binding on a genome wide scale and crystallization studies to determine the structure of WDR77. Aims 1. To check if WDR77 recognizes and binds to specific histone modifications. Peptide pull down assay Biotinylated (bait) peptides Immobilized on streptavidin beads Incubated with nuclear extract Collect beads Remove bound proteins by acid elution/ denaturation by heat References 1. Di Lorenzo, A. and M.T. Bedford, Histone arginine methylation. FEBS Letters, 2011. 585(13): p. 2024-2031. 2. Friesen, W.J., et al., A novel WD repeat protein component of the methylosome binds Sm proteins. J Biol Chem, 2002. 277(10): p. 8243-7. 3. Furuno, K., et al., Association of Polycomb group SUZ12 with WD-repeat protein MEP50 that binds to histone H2A selectively in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2006. 345(3): p. 1051-8. 4. Hosohata, K., et al., Purification and Identification of a Novel Complex Which Is Involved in Androgen Receptor-Dependent Transcription. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2003. 23(19): p. 7019-7029. 5. Le Guezennec, X., et al., MBD2/NuRD and MBD3/NuRD, two distinct complexes with different biochemical and functional properties. Mol Cell Biol, 2006. 26(3): p. 843-51. 6. Licciardo, P., et al., The FCP1 phosphatase interacts with RNA polymerase II and with MEP50 a component of the methylosome complex involved in the assembly of snRNP. Nucleic Acids Res, 2003. 31(3): p. 999-1005. 7. Margueron, R., et al., Role of the polycomb protein EED in the propagation of repressive histone marks. Nature, 2009. 461(7265): p. 762-7. 8. Peng, Y., et al., Androgen receptor coactivator p44/Mep50 in breast cancer growth and invasion. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2010. 14(12): p. 2780-2789. 9. Tee, W.W., et al., Prmt5 is essential for early mouse development and acts in the cytoplasm to maintain ES cell pluripotency. Genes & Development, 2010. 24(24): p. 2772-2777. Western blot 2. Purification of WDR77 and check its binding with PRMT5 and PRMT7 Figure 3 - H3K27me3 binding by EED (left and middle) and H3R2me2s binding by WDR5 (right), as shown from from crystal structures both at 1.9A. From Margureon et al. (2009) (left and middle) and Migliori et al. (submitted) (right). Constructs (Ernesto lab IMCB, Singapore) 1. WDR77-GST – pGEX6P1 2. PRMT7-GST – pGEX 3. PRMT5-His- pET32a Acknowledgements I would like to thank Dr. Martin Walsh for his invaluable guidance. I would also like to thank all members of the Walsh lab for helpful discussions about experiments and their unstinted support and encouragement.