* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7: Inside the Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
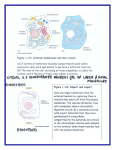
Chapter 7: Inside the Cell Text Vocabulary: Morphology Phylogeny Chromosome Nucleoid Genes Plasmids Ribosomes Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Cell Wall Glycolipids Flagella Fimbriae Cytosol Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Nuclear Lamina Nucleolus Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Lumen Smooth ER Golgi apparatus Cisternae Lysosomes Endomembrane System Vacuoles Peroxisomes Glyoxysomes Mitochondria Cristae Mitochondrial matrix Chloroplast Thylakoids Grana Stroma Endosymbiosis theory Differential centrifugation Nuclear pore complex Ribosomal RNAs Messenger RNAs Nuclear Localization Signal Pulse-chase experiment Culture ER signal sequence Signal recognition particle Glycosylation Glycoprotein Cisternal Maturation Endocytosis Exocytosis Receptor-Mediated endocytosis Early endosome Late endosome Nuclear lamins Autophagy Phagocytosis Bulk-phase endocytosis Microfilaments Actin filaments Motor protein Cytokinesis Cell crawling Intermediate filaments Microtubules Dimers Microtubule organizing center Centrosome Centrioles Cilia Kinesin Basal body Axoneme Lecture 8 PPT Review “Inside the Cell: The Dynamic Cell—Intracellular Transport” 1.) What is the central dogma in biology? (will be discussed in more detail in later lectures) 2.) How do proteins get targeted to their correct destination in the cell? 3.) Where does protein synthesis occur in the cell? How do mRNAs get out of the nucleus? How do nuclear proteins get into the nucleus? 4.) Outline as many components of the nucleus as you can—think about nuclear import, export, anatomy of nucleus, nucleic acid synthesis. 5.) What structures serve as a passageway into and out of the nucleus? 6.) What is the name of the amino acid sequence present in all nuclear proteins? What is its function? What family of proteins interacts with these amino acid sequences? 7.) Outline the steps in the endomembrane system using RNA that has just been synthesized/transcribed. 8.) What is the signal hypothesis? How does it explain the differences between the “signals” present within the AA sequence of an ER protein versus a nuclear protein? Include the modification to the ER protein that we discussed in class. 9.) What is glycosylation? What type of modification is this an example of? Be sure you can identify what the macromolecules are on this slide and any other example. 10.) Why would a protein travel from the ER to the golgi? What is the protein transported in? 11.) A protein designated for the lysosome would have what unique signal/tag/sequence within its amino acid sequence? Lecture 9 PPT Review “Inside the Cell: The Dynamic Cytoskeleton” 1.) Why would the cytoskeleton be characterized as dynamic? 2.) What are the three major elements of the cytoskeleton? Arrange them in order of greatest to smallest size. 3.) What is the globular protein that forms microfilaments? Describe subunits of this protein. Describe polarity for this protein? 4.) What is treadmilling? 5.) What is myosin classified as? How does it perform its function? What reaction is involved? 6.) What are 3 different types of movement that can occur through actin-myosin interactions? 7.) What is the primary protein that form intermediate filaments (that we discussed)? What are two functions of this protein? 8.) Describe polarity and “treadmilling” in intermediate filaments. 9.) What are the proteins that make up the composition of microtubules? 10.) List a few functions of microtubules? (There are two that were outlined in the PPT). Describe the polarity and “treadmilling” of microtubules. 11.) How are microtubules linked with the following: (Also list the motor proteins involved in each) a. Vesicle movement b. Whole cell movemen (think cilia + flagella) 12.) What is an axenome? 13.) Watch “The Inner Life of the Cell” and work on understanding each aspect of the video—always good to have a visual memory to refer back to when you get stuck on questions!