* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BACTERIA AND VIRUS REVIEW SHEET ANSWER KEY 1. In the
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
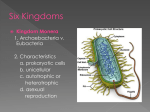
BACTERIA AND VIRUS REVIEW SHEET ANSWER KEY 1. In the following chart, fill in the six kingdoms and their basic characteristics. KINGDOM Cell Type Cellular Nutrition Organization Autotrophic & Archaebacteria Prokaryotic Unicellular Eubacteria Prokaryotic Unicellular Protista Eukaryotic Mostly Unicellular Fungi Plantae Animalia Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular 2. 3. 4. Heterotrophic Autotrophic & Heterotrophic Autotrophic & Heterotrophic Heterotrophic Autotrophic Heterotrophic Cell Wall Yes Yes, peptidoglycan Some with cellulose Yes, chitin Yes, cellulose No Examples Methanogens, halophiles Streptococcus, Tuberculosis Euglena, Amoeba Paramecium Mushroom, mold Tree, fern Human, insect The eyepiece magnifies an object 10x. The objective lens magnifies an object 4x. What is the total magnification? 40x If the objective above is swapped for a 10x objective, what is the new magnification? 100x Label the parts of the microscope below and briefly describe what each does. Eyepiece – magnifies the object 10x Course adjustment knob – focuses the object by moving the stage up and down Fine adjustment – focuses the object Objectives – magnify the object Stage – holds the slide Arm – supports the microscope Illuminator – lights the slide Base – supports the microscope 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Draw and describe the three common shapes and four arrangements of bacterial cells. Coccus – spherical Single Bacillus – rod Diplo – two Spirillum – spiral Strepto – chains Staphylo – clumps On the back of this sheet, make a chart listing the positive and negative contributions of bacteria to ecosystems. (next page) What is the major difference(s) between Archaebacteria and Eubacteria? Archaebacteria live in extreme habitats and Eubacteria live everywhere Archaebacteria do not have peptidoglycan in their cell walls and Eubacteria do. Explain how the cell type in prokaryotes differs from that in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes do not have nuclei or organelles, but eukaryotes do have a nucleus and other organelles (vacuoles, chloroplast, etc) Why are viruses considered nonliving? They cannot reproduce on their own, they do not grow, and they do not have metabolism What are the two major components of a viral particle? Genetic material (DNA or RNA) and a protein coat called a capsid Explain why certain viruses can only infect certain, specific types of host cells. The capsid is shaped to fit only certain cells like a lock and key What is a protist? Any organism that is not a plant, animal, fungus, or prokaryote On the back of this sheet, make a chart listing the positive and negative contributions of Protists to ecosystems. (next page) What are the three types of protists? How are they grouped into these categories? They are classified by their mode of nutrition: plant-like (autotrophic), animal-like (heterotrophic), fungus-like (decomposer) Draw and list an example of a protist with cilia, flagella, and a pseudopod. Cilia – tiny hair-like projections Flagella – long tail-like projection Pseudopod – “false feet” Stentor Euglena Amoeba 6. Make a chart listing the positive and negative contributions of bacteria to ecosystems. Positive Decomposition Produce oxygen through photosynthesis Nitrogen fixation Food products such as yogurt, cheese, saurkraut Live inside the digestive tract of mammals Clean sewage and oil spills Negative Pathogenic 13. Make a chart listing the positive and negative contributions of protists to ecosystems. Positive Produce oxygen through photosynthesis Phytoplankton are the basis of the aquatic food chain Diatoms used in road paint and toothpaste Algae used in conditioner, ice cream, sushi, deodorant Negative Pathogenic – malaria Dinoflagellates cause red tide Fungus-like protists caused the Great Potato Famine