* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (1) Quantitative traits and sequence variation Lecture objectives
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
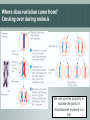
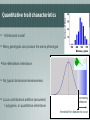
(1) Quantitative traits and sequence variation Lecture objectives 060313 0900:1200 By the end of this lecture you should be able to explain: • What genetic variation is and where it comes from • What SNPs are and what type of variation they encode • The difference between quantitative and qualitative traits (inc. e.g.s) • Why linkage disequilibrium might help you find important genes Genetics and variability • By sequencing genomes from related organisms we can estimate variation among or between species • Humans share 99.9% of their DNA: only 0.1% is variable! • The variable part is where we can potentially find an explanation for our phenotypic differences • Next-gen sequencing = enabling technology • Alleles and genes Genetics and variability • Alleles and genes • Alleles (allelomorph) are different forms of a gene occupying the same position (locus) on a chromosome • Different alleles are formed as a result of polymorphisms in the genes e.g. • a heterozygous locus will be biallelic, i.e. having both alleles of a gene Genetics & variationHomozygosis vs. Heterozygosis Ladies first Cross pollination Self pollination Plant A e.g. one pair of chromosomes ♀ Plant A ♂ ♀ pair is split x Plant B ♂ Meiosis re-association (F1) Identical chromosomes Identical genes homozygous Different chromosomes Different genes heterozygous Where does variation come from? Independent assortment of chromosomes Where does variation come from? Crossing over during meiosis We can use this property to localise the parts of chromosomes involved in a trait What does sequence variation look like? Mutations are maintained in linkage disequilibrium • Linkage: tendency of particular genetic loci to be inherited together • Linkage disequilibrium: non-random association of particular alleles Aim: understand the effect of alleles on traits vs What type of variation is found for traits? What links these? vs What links these? Qualitative trait characteristics • Follow Mendelian inheritance • Can predict the phenotype from the alleles carried • Often encoded by single genes e.g. Locus for eye colour with 2 alleles: B (dominant allele) and b (recessive allele) - four possible combinations: BB Bb bB bb Quantitative trait characteristics • • Infinitesimal model Many genotypes can produce the same phenotype • Non-Mendelian inheritance • No typical dominance/recessiveness • Locus contributions additive (assumed) = polygenic, or quantitative inheritance increasing disease threshold for disease to occur Quantitative trait loci and how to find them • Complexity of these traits, esp. those involved in adaptation probably arises from segregation of alleles at many interacting loci • Allelic effects are sensitive to the environment • Combination of molecular genetics and statistical techniques are needed to identify where these alleles are located The range of allelic effects Approaches for discovering the genetic basis of phenotypic variation • Quantitative trait loci analysis (QTL analysis) & eQTL analysis • related populations of organisms generated by a cross = recombinant inbred lines • Genome wide association studies GWAS • • • natural populations of a species random sample of individuals Statistical methods used to associate genotype (alleles) with trait Both rely heavily on accuracy in genotyping, trait measurement Next time: (2) Quantitative trait loci and genetic maps By the end of that lecture you should be able to explain: • The four main types of information you need to for QTL analysis • Why understanding recombination & genetic linkage is important for localising genes that control traits • What a marker-trait association is