* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Biology Chapter 12 Notes 12.1 Pedigrees A diagram that
Survey
Document related concepts
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
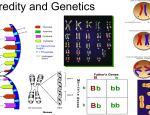
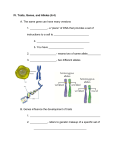
Honors Biology Chapter 12 Notes 12.1 Pedigrees A diagram that traces the inheritance of a particular trait through several generations Inferring Genotypes Knowing physical traits can determine what genes an individual is most likely to have. Predicting Disorders Record keeping helps scientists use pedigree analysis to study inheritance patterns, determine phenotypes, and ascertain genotypes. Recessive Genetic Disorders A recessive trait is expressed when the individual is homozygous recessive for the trait Cystic Fibrosis Affects the mucus-producing glands, digestive enzymes, and sweat glands Chloride ions are not absorbed into the cells of a person with cystic fibrosis but are excreted in the sweat. Without sufficient chloride ions in the cells, a thick mucus is secreted. Albinism Caused by altered genes, resulting in the absence of the skin pigment melanin in hair and eyes White hair Very pale skin Pink pupils Tay-Sachs Disease Caused by the absence of the enzymes responsible for breaking down fatty acids called gangliosides Gangliosides accumulate in the brain, inflating brain nerve cells and causing mental deterioration Galactosemia Recessive genetic disorder characterized by the inability of the body to digest galactose Dominant Genetic Disorders Huntington’s disease affects the nervous system. Achondroplasia is a genetic condition that causes small body size and limbs that are comparatively short. 12.2 Notes Incomplete Dominance The _______________________ phenotype is an ________________________ phenotype between the two homozygous phenotypes (both alleles are ____________________) Codominance Both alleles are _______________ in the _________________ condition (both alleles are seen at the same time) Sickle-cell Disease Changes in __________________ cause ______ blood cells to change to a _________ shape People who are ___________________ for the trait have both normal and sickle-shaped cells Multiple Alleles Blood groups in __________________ _________ blood groups have _________ forms of _______________. Coat Color of Rabbits _____________________ alleles can demonstrate a hierarchy of ___________________. In rabbits, ___________ alleles code for coat color: C, cch, ch, and c. Sex Determination Sex chromosomes determine an individual’s _________________. Sex-Linked Traits Genes located on the ___ chromosome ______________________ color blindness _______________________ Polygenic Traits ____________________ traits arise from the interaction of __________________ pairs of genes. Environmental Influences ___________________________ factors _____________ and exercise _______________ and water _________________________ Twin Studies Helps scientists separate genetic contributions from environmental contributions Traits that appear frequently in identical twins are at least partially controlled by heredity. Traits expressed differently in identical twins are strongly influenced by environment. Karyotype Studies ________________—micrograph in which the pairs of homologous chromosomes are ______________ in ____________________ size. Images of _____________________ stained during __________________ Chromosomes are arranged in decreasing size to produce a micrograph