* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Brain
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Superior colliculus wikipedia , lookup
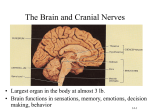
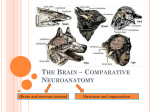
Chapter 4 Methods for Analyzing Brain Function - CAT or Computerized Axial Tomography (x-rays are passed through the head - rCBF or Regional Cerebral Bloodflow (uses radioactive isotopes injected into the blood. When a region of the brain is activated, more blood is sent to the area and the isotopes track this blood. The isotopes are measure by PET or Positron Emission Tomography) - fMRI or functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (detects the changes in oxygen bound hemoglobin) - Gene knockout approach (Genes that control certain brain functions can be altered and their effects studies) - Direct study of damaged brains and subsequent behavior (this is how psychobiology began) - Phrenology (associating behavior to different regions of the skull. Kind of archaic) The Nervous System - CNS or Central Nervous System (consists of only brain and spinal cord) - PNS or Peripheral Nervous System (nerves outside brain and spinal cord) The PNS has two divisions… 1. Somatic nervous system (the sensory and motor neurons) 2. Autonomic nervous system (controls heart, digestion and organs) The autonomic nervous system has two divisions… 1. Sympathetic nervous system (prepares organism for activity, fight-flight etc.) 2. Parasympathetic nervous system (facilitates vegetative responses such as digestion) - Bell-Magendie law (the spinal cord has attached dorsal roots that communicate sensory information and ventral roots that communicate motor information) - Grey matter (mostly cell bodies and dendrites) - White matter (mostly myleinated axons) Structure of the Brain - The brain is classified into 3 main areas… 1. The hindbrain (includes the medulla, pons and cerebellum) 2. The midbrain (includes the tectum, tegmentum, superior colliculus, inferior colliculus and substantia nigra) 3. The forebrain (includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, basal ganglia and cerebral cortex) Note: The brain is encased in a membrane called the meninges. The Hindbrain - Medulla ( controls vital reflexes like heart rate, breathing, coughing sneezing and salivating. The medulla is attached to the spinal cord via cranial nerves) - Pons ( is the crossover point between the left brain and right body and vise versa. Also has cranial nerve attachments) Note: The medulla and pons contain the reticular formation which conveys information from the brain to motor areas of the spinal cord. The reticular formation also directs the attention of the cerebral cortex. The medulla and pons also contain the Raphe system which has axons connected to much of the forebrain, thereby directing its response levels. - Cerebellum (controls the gracefulness and coordination of movements, timing and rhythm identification) The Midbrain - Tegmentum (includes the root of the 3rd and 4th cranial nerves, contains part of the reticular formation. It serves as a go between for the forebrain and hindbrain) - Substancia nigra ( gives rise to dopamine containing path) - Superior and inferior colliculus (important routes for sensory information) - Tectum (the roof of the midbrain and important information route) The Forebrain - Thalamus (processes and sends information to the cerebral cortex. The ocular nerves pass through here) - Hypothalamus (directs release of hormones from the pituitary gland and controls drinking, eating, fighting and sexual behavior) - Pituitary gland (hormones producing gland that releases hormones into the blood at the discretion of the hypothalamus) - Basal Ganglia (includes the structures caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus. Exchanges information with cerebral cortex, especially for memory, emotion, and behavior planning. Also influences movement) - Nucleus Basalis (information go-between from the hypothalamus and basal ganglia to the cerebral cortex. Plays a role in attention and intellect) - Hippocampus (stores certain memories) - Cerebral cortex The Ventricles - 4 fluid-filled cavities in the brain that provide cushioning and help to support the weight of the brain - Fluid is cerebro-spinal fluid The Cerebral Cortex (CC) - Corpus Callosum and anterior commisure (neurons that communicate with the opposite side of the brain) - Laminae (6 total layers running parallel to the cerebral cortex) - Columns of cells run perpendicular to the laminae - Occipital lobe (located at the posterior CC. AKA primary visual cortex) - Parietal lobe (located between the occipital and central sulcus. Contains the central sulcus and the postcentral gyrus. Controls touch sensations and information from muscle stretch receptors as well as touch and body location) - Temporal lobe (locate near the temples. Controls auditory information, perception of movement and facial recognition) - Frontal lobe (contains the primary motor cortex and prefrontal cortex. Controls fine movements. The prefrontal cortex receives information from all sensory systems and is important in delayed response tasks.