* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
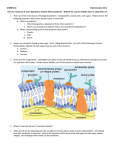
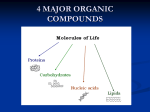
Carbon Compounds Organic Compounds: substances that contain both carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) Ex. Sugar – C2H12O6 Inorganic Compounds: substances that do not contain both carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) Ex. H2O and CO2 A. Organic Compounds C binds with other elements (H, O, N, P) to form monomers Monomer: a single compound with certain characteristics Polymer: long chains of monomers Synthesizing and Digesting Polymers Dehydration Synthesis: removing a water molecule from 2 or more monomers to make a polymer Hydrolysis: adding water to a polymer to split it apart into monomers (hydro = water, lysis = split) 1. Carbohydrates/Starch Polymer also known as a polysaccharide Monomers are sugars/saccharides (C6H12O6) Ring-shaped Glucose Fructose Monosaccharide = 1 sugar C6H12O6 (glucose) Disaccharride = 2 sugars C12H22O11 (sucrose) C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 = C12H22O11 + H2O Dehydration Synthesis Polysaccharide = many sugars (glycogen – in liver, cellulose – in plants) Ratio C : H : O 1:2:1 Ending: “-ose” for sugars and some starches Ex. Glucose, fructose, galactose (sugars), cellulose (starch in plants), glycogen (starch stored in the liver) Provide energy for cells Indicator: Iodine (tests for starch): yellow to blue/black Benedicts (tests for sugar): blue + heat changes to orange Digestive Enzyme: salivary amylase 2. Lipids Polymer also known as fat/oils Monomer: 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids Form straight chains of carbon Glycerol 3 Fatty Acids Non-Polar: repels water, no attractive force Used for long-term energy storage and forms waterproofs membranes Ending: “-ol”, “-one”, “-ide”, “-acid” Ex. Cholesterol, cortisol, testosterone, cortisone, triglycerides, Stearic Acid an Oleic Acid Digestive Enzyme: lipase 3. Nucleic Acid: (Polymer) Monomer: nucleotide (made of 3 parts) a. 5 carbon sugar b. Phosphate group c. Nitrogen base Stores and transmits genetic information, hereditary information, information to make proteins and other organic compounds, information to produce traits Ex. DNA and RNA Digestive Enzyme: Nuclease 4. Proteins: (Polymer) Monomer: amino acid – identified by an amino group (NH2) at one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) at the other end 20 different amino acids exist in nature Amino acids bind together to form a protein polymer by forming peptide bonds Form muscles, bones, hair, transport materials in and out of the cell, regulate the speed of chemical reactions (enzymes) Ending: “-ine” (for amino acids: monomer for proteins), “-in” for proteins, “-ase” for enzymes (protein polymers) Ex. Glycine, alanine, glutamine, fibrin, myosin, ***Enzymes (Catalyst) Protein that speeds up the synthesis or digestion of chemical compounds Specific in shape and specific for different compounds, can be reused Affected by temperature and pH Form Enzyme-Substrate Complex/Lock and Key Model Active Site: area of the enzyme in which the substrate (molecules) attach Denaturation: when temperature or pH changes the shape of the active site so that molecules can no longer attach Endings: “-ase” Ex. Amylase (starch) Lipase (lipids) Protease (proteins) Nuclease (nucleic acids)