* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules practice worksheet key
Survey
Document related concepts
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
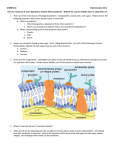
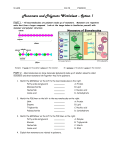
Last Name_____________________________ First Name______________________________ Macromolecule Worksheet 1. What are the definitions for a monomer and polymer? a. Monomer =a single building block similar in structure and repeating used to build a polymer. b. Polymer = many monomers linked together via covalent bonds. 2. Draw a polymer containing six monomers. Use pentagons as a monomer and label which is a monomer and a polymer. One monomer One polymer 3. What chemical reaction is used to make polymers? Break polymers? Dehydration synthesis reactions are used to make polymers from monomers and hydrolysis reactions are used to break polymers into monomers. 4. Complete the chart below. Organic Monomer Macromolecules Polymer Function Elements Examples Carbohydrates Monosaccharide polysaccharide Fuel source C, O, H Glucose, fructose, starch, glycogen Lipids Building blocks =glycerol + fatty acid chains Not a polymer, but still an organic cmpd. like the others Energy storage (TG’s); form cell membranes (phospholipids) C,O,H, and sometimes P Linoleic acid, arachadonic acid Proteins Amino acid polypeptide Enzymes, receptors, transport proteins C,O,H, N and sometimes S Hydrolase, Store genetic material; C,O,H, P, N DNA, RNA Nucleic Acids nucleotides polynucleotide 1 Oxidase Hemoglobin 5. Why are the chemical shapes of lipids different between saturated and unsaturated fats? Saturated fats have the maximum amount of hydrogens bound to the carbons of the F.A. chains, therefore, they lack double bonds and can pack tightly forming solids at room temp. and unsaturated fats have less hydrogens bound to the carbons of F.A. chains, therefore, they do have double bonds and do not pack tightly forming liquids at R.T. 6. Circle Answer: Are lipids polar or non-polar? Polar Are lipids soluble in water? Non-polar Yes No 7. Draw the general chemical structure of an amino acid. Put a box around the portion of the amino acid that varies from other amino acids, and then discuss the differences. The R group varies from amino acid to amino acid giving them different chemical properties that range from acidic to basic and hydrophilic and hydrophobic. 8. What kind of bond holds amino acids together in a polymer? A specific type of covalent bond called a peptide bond. 9. What are the three parts that make up a nucleotide? a. _____pentose sugar Draw one DNA nucleotide. b. _____nitrogenous base c. _____Phosphate group What are two functions of DNA? d. _____stores genetic material________________________________________________ e. _____carries instructions to make cellular proteins_______________________________ 10. What are the two types of sugars found in nucleic acids and their corresponding polymer? DNA sugar___deoxyribose_____________ RNA sugar____ribose________________ 2 What are the four bases for DNA? _______cytosine___________________ What are the four bases for RNA? _______ cytosine ________________ _______guanine___________________ ________ guanine _______________ _______adenine___________________ _________ adenine ______________ _______thymine___________________ _________uracil_________________ 3