* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon Compounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
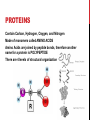
CARBON COMPOUNDS CHAPTER 2, SECTION 3 CARBON is the principle element in the large molecules that organisms make and use ORGANIC compounds contain carbon INORGANIC compounds are all the other compounds 4 valence electrons and can easily bond Carbon has _____ with other atoms to make large, complex molecules Most complex macromolecules are POLYMERS which are made up of smaller units called MONOMERS CARBOHYDRATES Contain Carbon, Hydrogen, & Oxygen Sugars and Starches Store chemical ENERGY and have some structural purposes Variable in Size SMALL MONOMER LARGE POLYMER Monosaccharide Simple Sugars EX: Glucose Disaccharide Glucose + Fructose = SUCROSE Polysaccharide Many Glucose = STARCH CARBOHYDRATES POLAR molecules, but solubility in water depends on size Simple sugars such as glucose supply immediate energy for cell activities Living things store extra sugar as complex carbohydrates such as starch or glycogen LIPIDS Contain mostly Carbon and Hydrogen Fats, Oils, and Waxes Store ENERGY and are a structural component of biological MEMBRANES NONPOLAR molecules formed from a Glycerol molecule and Fatty Acid Chains NUCLEIC ACIDS Contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous Molecules of INHERITANCE (DNA and RNA) Assembled from monomers called NUCLEOTIDES PROTEINS Contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen Made of monomers called AMINO ACIDS Amino Acids are joined by peptide bonds, therefore another name for a protein is POLYPEPTIDE There are 4 levels of structural organization PROTEINS Proteins are very diverse and have different functions: Aid in chemical reactions (enzymes) Help fight disease (antibodies) Build bone and muscle tissue Help transport substances in/out of cell Help regulate cell processes