* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry-lab-identifying
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
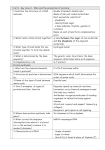
Macromolecules: Identifying Carbohydrates and Proteins Introduction and Background information: Atoms are pure substances like Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus. Scientists use the Periodic Table of Elements to organize all pure substances on earth. Elements often join together (or bond) through donating or sharing energy from electrons. When two or more elements join together we call this a molecule. All living things are made a handful of the same molecules. The molecules essential for life to function are called biomolecules and are considered “organic”. Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus are the five essential biomolecules. When big and bulky long chains of essential molecules bond together they are called MACROMOLECULES. There are 4 categories of macromolecules that are found in all living things: proteins, carbohydrate, lipids and nucleic acids. Lab Objective: To identify what kinds of food sources contain which category of macromolecule such as proteins and carbohydrates (sugar and starches). Indicators are chemicals that will change color, form a precipitate (residue) or bubble in the presence of specific molecules Benedicts: Tests for Sugar carbohydrates. It will turn from blue to green-yellow or orange the presence of sugars. The more yellow – the more sugar is present. Lugols (Iodine): Tests for starch. It will turn from yellow-brown to purple-green to indicate a starch is present. Biurets: Tests for Proteins. It will turn from Blue –purple to a pink-orange Background Information: 1. What are Proteins? There is no life without protein. Next to water, protein is the most plentiful substance in your body.Proteins are found in every part of your body, the skin, muscles, hair, blood, body organs, eyes, even saliva. Protein is composed of smaller N-H groups known as amino acids. Food sources for protein include beef, poultry, fish, and green vegetables. These amino acid chains inside a protein are called a peptide chain. Amino acids are like the individual Lego bricks that fit together to build a bigger structure. Therefore, amino acids are often called the “building blocks of protein.” There are more than 20 different amino acids. The suffixes -in, -ine identify a protein, amino acid or nucleic acid. Examples: vitamin, pepsin, insulin, tyrosine, adenosine, adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine. Proteins are macromolecules containing the element Nitrogen hooked to Carbon molecules. A protein is composed of several amino acids (N-H) molecule groups that are linked together. Proteins have different functions; they can provide structure (ligaments, fingernails, hair), help in digestion (stomach enzymes), aid in movement (muscles), help us fight off infection and disease and play a part in our ability to see (the lens of our eyes is pure crystalline protein). Protein forms the structural material of bodily tissues. Protein control critical physiological function. Protein is used in the body to build, maintain, and repair body tissues. Protein energy will be used only after other energy sources (carbohydrate and fat) are exhausted or unavailable. 2. The Structure of an amino acid building block. ***Look for the Nitrogen functional group attached to the Carbons to identify the protein molecular structure. Proteins can have different special shapes. Nucleic acid structures are smaller than the larger, sometimes floppy proteins. Often, proteins can bend, stretch, fold, spiral or form branches. Think about how hair can be straight, wavy, bouncy, curly, shiny and different colors. These characteristics are from the proteins that found inside the hair! 3. ENZYMES- are special protein starters - (we will not be testing for these today) Enzymes are special biological proteins (found in all living things). Enzymes start, end and control all the body functions like digestion, growth and development, and even dying. Enzymes are known as “biological catalysts.” A catalyst reduces the time in a chemical reaction in breaking apart or changing the shape of molecules. Vitamins, like B6, are catalysts in the body. Many vitamins like A,B,C,D,E, and K are necessary for a healthy life. Therefore, using an enzyme will lower the energy to start a reaction (called activation energy) and make the reaction move faster than if a chemical reaction did not have an enzyme starter. Enzymes are usually identified by the suffix –ASE. For Example: sucrase enzyme breaks apart sucrose sugar. Lactase enzyme breaks apart lactose sugar and Amylase enzyme breaks apart amylose sugar. II. What are Carbohydrate? A carbohydrate is a compound called a saccharide and is made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. For animals, such as humans, carbohydrates are the fuel source to release an energy molecule called ATP. Instead, carbohydrates are both a fuel and a support structures. Carbohydrates can be categorized as simple sugars, starches and cellulose. Simple Sugars are “monosaccharide” food sources that release energy and include honey, jams, jellies, syrup, table sugar, candies soft drinks, fruits, and fruit juices. The body energy we get from sugar is a molecule called glucose. Sugars like table sugar (sucrose), sugar in candy (dextrose) and sugar in fruit (fructose) can readily be broken apart and converted into glucose by enzymes in different parts of the body. Starch is the building material for plants and is used for support and structure. Some examples of starches are wood, potato, potato chips, French fries, flour, grains, rice and bread. Starches are often sticky like glue, hold things in place, and are edible. It takes a little longer for the body to digest starches but they can be reduced into glucose. Cellulose is unique. Cellulose is a sugar but acts like a starch. In other words, cellulose is a sugary energy source and a building material for plants…it is the chief component in stems, tree trunks, leaves and plant cell walls. Cotton is a pure form of cellulose and it can be woven into fibers. We eat corn, but we wear cotton. Unfortunately, human do not have the correct enzymes to break apart cellulose in our stomachs. Cows and organisms inside a termite stomach can digest cellulose. In our stomachs, undigested plant materials such as, corn, passes through our stomach and intestines almost untouched. Monosaccharide =1 sugar ring, disaccharide =2 sugar rings polysaccharide =several sugar rings 1. Structure of Carbohydrates Notice the CHO…straight chains or branches are starches. Sugars have a rings forming 5 or 6 carbons - The suffix -OSE means sugar Method: 1) Label all your test tubes. Write the food on each test tube in your experimental group. Label one test tube as water. This is your control group. 2) Add 10 ml of water to every test tube. The water level is a constant variable 3) Place a small quantity of a food item in each of the different experimental test-tube (the amount is about the size of a pencil eraser.) 4) Add 2 pipettes of the indicator you were assigned into each test tube. Draw your “before heat” test tube observations. Use color pencils. 5) Place all tubes in a beaker with water and heat for 3 minutes. Draw your “after heat ” test tube observations. 6) Clean your test tubes and rinse out your test tubes. 7) Repeat steps 1-6 with each of the other indicator Post Macromolecules Lab Questions for your Lab Report 1) What is the objective of this lab? (Topic Sentence) 2) Identify the two macromolecules we tested for in this lab (Introduction Paragraph) 3) Identify the Experimental Group: _______________________________ 4) Identify the Independent Variable: ______________________________ 5) Identify the Dependent Variable: _______________________________(measured and responds) 6) Identify the Control Group: ________________________________ 7) What is the function of the control group? ______________________________ 8) Describe control factors that we kept constant (the same or equal) 9) Complete the background knowledge chart for each of these macromolecules. (Supporting paragraph in the Introduction with facts) Macromolecule List 2 Describe the 2 source where What Describe the examples of function(s) of you can find in essential indicator and the this this foods this elements color change that macromolecule macromolecule. macromolecule make up the will occur if this molecular molecule is present structure? in a food source Ending with – ine, in, or ase Protein Carbohydrate Ending with Sugar -ose Carbohydrate -ide Starch 10) Your Reflection on this lab: (This will be part of your Conclusion) Yes, you may write sideways for more room. Did you like Describe two How do you How were your How has this lab this lab? Why things you think repeating results the same changed your or why not? learned from this experiment or different knowledge observing your might provide when you about test tubes. different compared your macromolecules Identify which results? results to test please. another team?