* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 SWBATS Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Cryobiology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
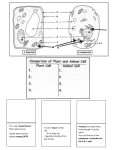
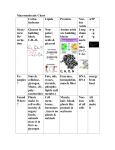
Chapter 2 SWBATS What three subatomic particles make up atoms? How are all of the isotopes of an element similar? What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? How do energy changes affect whether a chemical reaction will occur? Why are enzymes important to living things? Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. h. Students know most macromolecules (polysaccharides, nucleic acids, proteins, lipids) in cells and organisms are synthesized from a small collection of simple precursors. e. Students know proteins can differ from one another in the number and sequence of amino acids.