* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
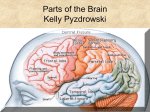
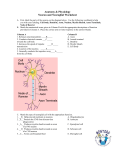
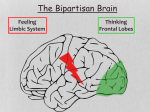
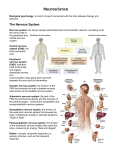
Psyc103-019 Introduction to Psychological Science Dr. Jen Wright Fall, 2008 Chapter Questions Ch. 3: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. What is a neuron? Please describe the parts of a neuron and what they do. Also describe the three major types of neurons and their function. 2. What is the myelin sheath and why is it so important to neural functioning? What do you think happens when the myelin sheath is damaged or destroyed? 3. Explain how neuronal communication involves both electrical and chemical signaling. 4. What are neurotransmitters? Pick one neurotransmitter and explain its importance to everyday physical/psychological functioning (including when it malfunctions). 5. Explain how drugs work as either agonists or antagonists in the brain. 6. Take a look at Figure 3.9. Please explain the importance of both subdivisions of the ANS to our daily functioning. In particular, what is something that commonly happens when these two subdivisions aren’t properly balanced? 7. Briefly describe the functional difference between the three major brain regions: the hindbrain, the midbrain, and the forebrain. Which is the oldest and which the youngest regions of the brain? 8. What does the limbic system regulate and what parts of the brain does it include? 9. What is the corpus callosum and what does it do? (When you get to page 109, come back to this question – what sorts of strange things happen to people when the corpus callosum is damaged or severed?) 10. What are the four lobes of the cerebral cortex? Please describe briefly their functions. 11. In which lobes are the motor and somatosensory cortexes located? What are their functions? And why do you think the two areas are located right next to one another? 12. What parts of the body are most strongly represented in the motor cortex? In the somatosensory cortex? Why do you think this is the case? 13. What do the authors of the text mean when they say the “brain is plastic”? Give an example. 14. Please explain the difference between the ontogeny and phylogeny of the brain. 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, and an fMRI? How do these machines help us to better understand the brain? How do they help us to better understand the mind? GROUP Extra Credit – 2.5 pts: The limbic system includes both the hippocampus and the amygdala. What do you think the significance of this is? What does it tell us about the evolutionary relationship between emotions and memory? GROUP DEBATE QUESTION: Human infants are born with only 25% of their brain development completed (whereas for all other species brain development at birth is more like 75% complete). So, there is a lot of brain development that happens when a child is young – most of it in the first 5 years of life! This means that the child’s developing brain is highly “plastic” and is powerfully influenced (either positively or negatively) by the environment the child is raised in. Knowing this, do you think society should allow children to be raised in impoverished/dangerous environments?