* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
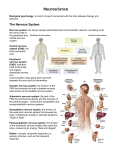
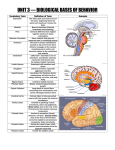
Name: _______________________________________________ Hour: _____ Group Name and Number: __________________________________________ Matching: Please match each part of the brain to its definition using the word bank. 1 point for each correct answer. WORD BANK A. cerebellum B. limbic system C. pituitary gland D. hypothalamus E. cerebral cortex F. amygdala G. reticular formation H. medulla I. hippocampus J. corpus callosum K. Wernicke’s area L. temporal lobes M. parietal lobes N. occipital lobes O. thalamus P. brainstem Q. frontal lobes R. neuron S. dendrite T. spinal cord U. motor cortex V. endorphins W. axon X. myelin sheath Y. action potential Z. synapse AA. neurotransmitters BB. dopamine CC. acetylcholine DD. norepinephrine EE. Broca’s area FF. serotonin _______ 1. the oldest part and central core of the brain, responsible for automatic survival functions. _______ 2. the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. _______ 3. controls language reception – a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe. _______ 4. the brain’s sensory switchboard. It directs messages to the sensory receiving areas of the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. _______ 5. a structure in the limbic system linked to memory. _______ 6. the master endocrine gland. _______ 7. includes the visual areas, which receive visual information from the opposite visual field. _______ 8. a nerve network in the brain stem that plays an important role in controlling arousal. _______ 9. “morphine within” – a natural, opiatelike neurotransmitter linked to pain control and to pleasure. _______ 10. associated with emotions such as fear and aggression. Includes the hippocampus, amygdala and hypothalamus. _______ 11. pathway for neural fibers traveling to and from brain; controls simple reflexes. _______ 12. a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. _______ 13. axon fibers connecting two cerebral hemispheres _______ 14. two almond-shaped neural clusters that are linked to emotion. _______ 15. controls language expression – an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movement of speech. _______ 16. directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking and sleeping. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. _______ 17. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body positions. _______ 18. an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. _______ 19. neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. _______ 20. the body’s ultimate control center and information-processing center. _______ 21. the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands. _______ 22. neurotransmitter that helps control alertness and arousal. _______ 23. neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning and memory. _______ 24. the base of the brainstem that controls the heartbeat and breathing. _______ 25. the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. _______ 26. a layer of fatty tissue encasing the segmented fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next. _______ 27. this is attached to the rear of the brainstem and helps coordinate voluntary movement and balance. _______ 28. involved in speaking, muscle movements and in making plans and/or judgments. _______ 29. neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. _______ 30. chemical messengers that travel between neurons. _______ 31. a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. _______ 32. includes the auditory areas, each of which receives auditory information from the opposite ear.







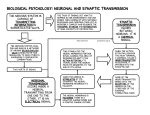



![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)