* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensory Physiology
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
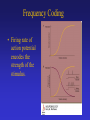
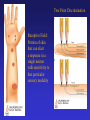
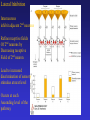
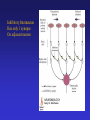
Sensory Physiology Concepts To Understand Receptor Potential Amplitude Coding Frequency Coding Activation/Inactivation Neural Adaptation Synaptic Depression Synaptic Depression Receptive Field Primary: Always On Secondary:Center:On/Surround:Off Lateral Inhibition 2-point Discrimination Sharpening Receptive Field Classification of Sensory Receptors • Nomenclature based on • Nomenclature based on sensory stimulus source type of sensory stimulus • Exteroreceptor • Interoreceptor • Propioceptive receptor • • • • • • Mechanoreceptor Chemoreceptor Thermoreceptor Nocireceptor Photoreceptor Electroreceptor How to Code the Stimulus Strength • Amplitude Coding • Frequency Coding • Population Coding – How many neurons responded to stimulus? • Sensitivity of Neurons – Did you activate neurons with low as well as high threshold for activation? Receptor Potential: the neuron’s electrical response to the Sensory stimulus Leads to an action potential in the primary or 2nd sensory neuron Amplitude Coding • The amplitude of the receptor potential increases as the sensory input increases • It modifies the firing rate of action potential • The size of the receptor potential gives information about the strength of the sensory stimulus. Action Potential Firing Rate • The steady state rate of action potential firing can increase or decrease in frequency known as “On” pathway and “Off” pathway. • Secondary neurons can receive inputs from both “on” and “off” neurons and that leads to more sensitivity. Frequency Coding • Firing rate of action potential encodes the strength of the stimulus. Concepts To Understand Receptor Potential Amplitude Coding Frequency Coding Activation/Inactivation Neural Adaptation Synaptic Depression Synaptic Depression Receptive Field Primary: Always On Secondary:Center:On/Surround:Off Lateral Inhibition 2-point Discrimination Sharpening Receptive Field Two Point Discrimination Receptive Field: Portion of skin that can elicit a response in a single neuron with sensitivity to that particular sensory modality Lateral Inhibition Interneurons inhibit adjacent 2nd neurons Refine receptive fields Of 2nd neurons by Decreasing receptive Field of 2nd neuron Lead to increased discrimination of sensory stimulus at next level Occurs at each Ascending level of the pathway Increased Information Input 2nd Sensory Neurons Can be influenced by Input outside the receptive Field for their primary Receptor neurons by synaptic Connection from interneurons Activated by adjacent primary Receptor neurons. 2nd sensory neurons have Smaller more refined Receptive fields than the Primary sensory receptor neuron Somatosensory neuron in somatosensory cortex has a more refined receptive field area than the primary sensory receptor neuron in the periphery that responds to the stimuls. Cortical somatosensory neurons also have more complex and selective stimulus requirements for responses, such as a specific of movement Direction Sensitive Coritical Neurons in S1 somatosensory cortex Inhibitory Interneuron Has only 1 synapse On adjacent neuron