* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam - UF Psychology
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
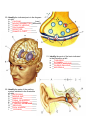
Physiological Psychology Dr. Donald J. Stehouwer Name_____________________________ Spring 2012 Answer Key— Final Exam On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid in doing this assignment." (signed) _____________________________ FILL IN THE BLANKS: 1. Provide the correct terms defined below: __rostral__________________ toward the nose __medial__________________ toward the midline __afferent__________________ projecting toward a point of reference __ipsilateral__________________ on the same side of the body 2. The ventricles of the brain are filled with the fluid called _cerebrospinal fluid_________________, which is made in a specialized bed of blood vessels that lines the ventricles called the _choroid plexus_____________. 3. The part of the eye that does the major, coarse focusing of light is the __cornea___________________. 4. Two competing theories of color vision are the __trichromatic theory_____________, which is based on the relative activity of the different kinds of retinal cones, and the __opponent process theory_______________, which is suggested by receptive fields with center-surround antagonism of complementary colors. 5. The greater incidence of mounting behavior in male than in female rats is thought to reflect ___masculinization______________ of the brain. The lesser incidence of lordosis in male than in female rats is thought to reflect __defeminization______________ of the brain. 6. Two rapidly-adapting cutaneous receptors that are particularly responsive to vibration are _Pacinian corpuscles____________ and __Meissner’s corpuscles___________. TRUE-FALSE: Fill in the "O" to indicate whether each alternative is True (T) or False (F). T F X O X O X O X O X O X X O O O 8. Postsynaptic potentials O a. decay (become smaller) with distance from the synapse. O b. usually must summate to become suprathreshold. X c. that are generated on the soma are more likely to be inhibitory than excitatory. X d. may involve second messenger systems at iontropic synapses. X e. are generated mainly in the axon hillock and axon. 7. Functions common to most neurons include a. receiving and integrating inputs. b. causing muscluar contractions. c. transmitting information to target cells. d. responding to sensory stimuli. e. conducting action potentials. T F X X X X O O O O O X X O O X O X X O 9. Among the functions of glial cells are a. providing mechanical support for neurons. b. forming scars in areas of brain damage. c. transporting nutrients and wastes between neurons and the blood. d. acting as phagocytes. e. conducting action potentials. O 10. The catecholamine theory of mood a. explains why amphetamine is a mood-elevating drug. b . arose primarily from studies of the effects of atropine on emotions. c . provides an explanation of how chlorpromazine produces its psychological effects. d . suggests that one should decrease the level of activity in CA systems to alleviate depression. X e. explains why schizophrenics experience auditory hallucinations. X X O X O O O X O X 11. Addiction to a drug a. results in acute withdrawal symptoms that are usually treated pharmacologically. b. to one substance may result in tolerance to other drugs. c. is completely reversible following prolonged periods of absitnence. d . typically involves both craving and a physiological need for the drug. e . occurs only with tobacco and narcotics, whereas psychological dependence can develop to any drug. X O X O O O X O X X 12. In the human visual system a . information from temporal ganglion cells projects to the opposite hemisphere. b. inputs from the two eyes converge on neurons in the lateral geniculate body. c. form and color of an object are processed in parallel with its movement and location. d. the retinotectal pathway is critical to analysis of the biological relevance of a stimulus. e. primary visual cortex contains cells that are responsive to very complex and specific features in the envrionment (e.g. “grandmother cells”). X X X O O 13. Lateral inhibition is O a . found between the center and surround regions of a retinal ganglion cell receptive field. O b. found between adjacent glomeruli of the olfactory system. O c. found in the organization of cutaneous receptive fields. X d. produced by 1b afferents arising from Golgi tendon organs. X e. another name for reciprocal inhibition in motor systems. X X O X X X X O O O O O X O O 14. Pain can be controlled by a . activation of the spinomesencephalic pathway. b. activation of cells in the periaqueductal gray. c. inhibition of serotonergic (5-HT) cells that project to the spinal cord. d. activation of non-pain afferent fibers. e. gently rubbing or stroking the painful area. O O X X X 15. The adrenal medulla a. secretes adrenalin. b. is innervated by preganglionic sympathetic axons. c. is important for regulating glucose metabolism. d. secrets insulin. e. is controlled by the hypothalamus via ACTH secreted from the anterior pituitary. T F O O X O X X X O X O X O X O O 16. The children of a woman on a diet deficient in iodine would likely be a. albinos. b. jaundiced. c . cretins. d. less masculine (if male). e. developmentally delayed. 17 A female rodent fetus located between two male fetuses in the uterus O a. is likely to have a higher fetal level of testosterone in her blood than a female that is located between two females. X b. is likely to mate with one of those males in adulthood O c. is more likely to show male-typical sexual behavior in adulthood than a female that was located between two females. X d. will be highly emotional as an adult as a result of the stress from being between two males as a fetus. X e. will compensate by developing a more female-type brain (demasculinization). 18 Match each cranial nerve with its number (not all items in the right column will be used __G____ I A. abducens __F____ III B. auditory __J____ V C. facial __B____ VIII D. glossopharyngeal __D____ IX E. hypoglossal __L____ X F. oculomotor G. olfactory H. optic I. spinal accessory J. trigeminal K. trochlear L. vagus 19. Match the name of each person with his contribution to the study of the brain and behavior. _F____Lashley A. brain is an organ to cool the blood _J____Descartes B. law of specific nerve energies _K____Gall C. gross anatomy of nervous system _D____Ramon y Cajal D. neuron doctrine _H____Hebb E. acetylcholine transmitter from nerve to heart _G____Helmholtz F. Law of Mass Action; Law of Equipotentiality G. speed of conduction of nerve impulse H. synaptic mechanism of learning I. electricity produced by frog’s leg J. First mechanistic explanation of behavior, mind/brain dualism K. correlated skull shape and personality characteristics 20. Identify the indicated parts in the diagram at right A. __CALCIUM_______________(ions)_ B. __NEUROTRANSMITTER_molecules) C. __SYNAPTIC VESICLE________ D. __ION CHANNEL________ E. __RECEPTOR______________ F. __SYNAPTIC CLEFT__________ 21. Identify the parts of the brain indicated in the illustration at left. a. __THALAMUS_________________ b. __PUTAMEN________________ c. __CAUDATE NUCLEUS_________ d. __GLOBUS PALLIDUS___________ e. __AMYGDALA________________ 22. Identify the parts of the auditory system indicated in the illustration at right. A. __OUTER EAR______________ B. __MIDDLE EAR_____________ C. __INNER EAR_______________ D. __PINNA_OR AURICLE_______ E. __AUDITORY CANAL_________ F. __TYMPANIC MEMBRANE_____ G. __OSSICLES_______________ H. __OVAL WINDOW___________ I. ___COCHLEA_______________