* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Downing Science 10
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
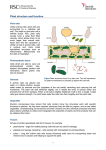
Science 10 – Unit C - BIOLOGY Chapter 3 - Plants C3.1 - Cells, Tissues and Systems Cells, Tissues, and Systems o In all living systems, co-operation ensures that needs are met, that all cells: Unicellularity vs Multicellularity Unicellular Organisms o All life processes occur o volume ratio Multicellular Organisms o Contain specialized cells that surface area to o o tissues, organs, organ systems surface area to volume ratio o Plant Organization o Like animals, plants have an organization Cells Tissues - group of specialized cells Organs - tissues Organ System - group of o Practice problems: Put these terms in order from smallest (most specific) to largest (least specific) lungs, bronchiole, mitochondria, respiratory system, lung cells leaf cell, chloroplasts, palisade tissue, shoot system, leaf in each example above, what is the organ? what is the organ system? what is the tissue? Plant Organ Systems o Plants have two organ systems The shoot system: includes also includes contains photosynthetic organs that The root system: also includes aerial roots absorbs o Practice problem: Put the letter S next to any part of the plant that is part of the shoot system, and R for the root system Plant Growth o Plant cells divide for new growth and to o mitosis: process of cell division where unlike in animal cells, mitosis in plants requires growing cell division occurs in growth areas called when new cells are produced in the meristems, they have the potential to Plant Structure o Plants contain materials which give them strength and support cellulose gives plant cell walls structure lignin is another supportive material found in plants newsprint made from trees with a high lignin content, and it is the lignin that it is responsible for high quality, bright white paper has Plant Tissue o Dermal tissue (epidermis) found on the outside of herbaceous plants (non-woody) produces a cuticle: involved with matter and gas exchange o Ground tissue layer responsible for photosynthesis and food & water storage makes up most of the body of the plant some cells are tightly organized some cells are loosely packed to allow for o Vascular tissue responsible for the transportation of materials Xylem: moves Phloem: distributes vascular bundles are Vascular Tissue o Xylem tissue: moves water and dissolved minerals movement transports for photosynthesis made of long individual cells which grow holes at each end and fuse like a long straw xylem cells die, but o Phloem tissue: moves dissolved sugars (food) formed with long individual perforated ends and sides to allow transfer of nutrients by osmosis companion cells located in the phloem tissue use ATP to move and transport nutrients from to Specialization in Plant Cells o Specialized cells make products that are Example 1: cells in the root system are responsible for absorbing water and minerals these cells grow tiny hairs called root hairs to maximize surface area. Example 2: dermal cells produce a cuticle to protect the plant from Example 3: guard cells form tiny pores called stomata on the underside of plant leaves formed from the plant’s stomata are involved in Homework - Read p.296 – 302, o complete diagram o complete Section C3.1 in green workbook Transport in Plants Identify the structures that make up the shoot and root systems, and the processes occurring in each structure that are responsible for transport in the plant. Science 10 – Unit C - BIOLOGY Chapter 3 - Plants C3.2 - The leaf and photosynthesis Photosynthesis o The leaf is a collection of tissues working together to carry out “Photo” = light, “synthesis” = putting together “photosynthesis” = o The purpose of photosynthesis is Water + Carbon Dioxide ----------- Glucose + Oxygen chlorophyll + light 6 H2O(l) + 6 CO2(g) -------------------> C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) chlorophyll + light Chloroplast o Plant cells have organelles called , which contain o cells containing chloroplasts are found in the ground tissue o light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and turned into chemical energy (food for the plant) o Accessory Pigments Chlorophyll is not the only pigment to capture light energy Accessory pigments help protect the plant and when temperatures get colder in the fall, Gas exchange in plants o Two main reactions that take place in plants and produce gases as products Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts Occurs Produces Cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria (as long as products from photosynthesis are available) Glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 CO2 + H2O + energy o Photorespiration the two processes together o Observing photosynthesis What is an easy way to measure photosynthesis? Watch for a product of photosynthesis – OXYGEN Homework: read p.303 – 308 o complete section C3.2 in the green workbook