* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
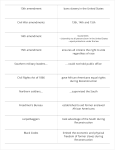
The Impact of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments With the end of the Civil War came freedom for over four million enslaved African Americans. This great movement of freedom that started with the signing of the Emancipation Proclamation was finally completed in December of 1865 with the ratification, or approval, of the 13th Amendment. The 13th Amendment abolished slavery in the United States and its territories forever. With this amendment, many in the North hoped that the effects of slavery would fade quickly. Instead, Southern states found new ways of controlling former enslaved African Americans. What happened at the end of the Civil War? What was important about the 13th Amendment? What did the North hope this amendment would do? The period of Reconstruction. history following the Civil War is known as During this period, Congress passed laws to help rebuild the nation and bring the Southern states back into the Union. An organization called the Freedmen’s Bureau was set up by Congress to help former enslaved African Americans build new lives. It provided food, clothing, shelter, medicine, and schools. What is the period of history following the Civil War called? What did Congress do during this period of time? What was the Freedmen’s Bureau? During Reconstruction, African Americans began to exercise their newfound freedoms. They could hold government positions, eat in the same restaurants as whites, ride in the same railway cars, use the same public facilities, and vote in the same elections. This, however, did not last. White citizens soon became concerned by these new freedoms and began to take steps to limit the rights of African Americans. African Americans began to feel the effects of discrimination as the freedoms and rights promised to them were taken away by many Southern states. Discrimination is the unfair difference in the treatment of people. Once again African Americans were not allowed to vote, hold office, use public facilities with whites, or attend white schools. How did African Americans exercise their newfound freedoms? Why were the rights of African Americans limited again? What did African Americans begin to feel the effects of? What is discrimination? What happened as a result of discrimination? Before long, Congress became troubled at how African Americans were being treated and they voted on a new, tougher plan for Reconstruction. Part of this plan included the Civil Rights Act of 1866. It declared that all Americans were citizens and everyone had the same rights. In addition, the new state governments were thrown out and Southern military leaders were not allowed to hold any offices. The Civil Rights Act of 1866 was enforced by federal troops, or the Northern soldiers whose job was to make sure the South followed this plan. Union officers served as governors of the Southern states. In order to return to the Union, Southern states had to rewrite their constitutions to give all men the right to vote. They also had to approve the 14th Amendment to the Constitution. The 14th amendment gave citizenship to all persons born in the United States and equal protection under the law. Why was Congress troubled? What was the Civil Rights Act of 1866? How was the Civil Rights Act of 1866 enforced? How could this legislation change the life of the African American? What was the 14th Amendment to the Constitution? During this period of Reconstruction, some people from the Northern states went to the South to make money. These Northerners were called carpetbaggers because they arrived carrying their belongings in suitcases made of carpeting. They opened businesses and bought land at cheap prices. Farmers, whose land had been ruined by the war and who had no money except for worthless Confederate currency, could not afford to pay the taxes on their land. In many cases, carpetbaggers bought the land by simply paying as little as $25.00 in back taxes. Southerners resented the carpetbaggers for taking advantage of the South during this difficult time. Why did Northerners move to the South to make money? What were carpetbaggers? Why did Southerners resent the carpetbaggers? Eventually, another amendment was added to protect the rights and freedoms of all American citizens. The 15th Amendment ensured that all citizens had the right to vote regardless of their race, their color, or the fact that they were once slaves. With the approval of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments, equal protection under the law was finally guaranteed for all citizens of the United States. What was the 15th Amendment to the Constitution? How would the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments change the lives of African Americans? Reconstruction ended with the Election of 1876. President Rutherford B. Hayes removed federal troops from the South. Without this strong supervision, Southern states reverted, or went back to many of the practices seen right after the Civil War. The rights that African Americans had gained during Reconstruction were lost once again through the Black Codes. The Black Codes were laws, which once again, restricted the civil rights of African Americans. When did Reconstruction end? What happened when President Rutherford B. Hayes took office? What were the Black Codes?