* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Development of States and Empires
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
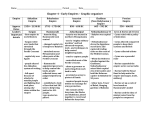
The Development of States and Empires By: Kaitlyn Coleman, Aubra Ladd, Tiffany Owens, and Kevin Walters Southwest Asia: Persian Empire ● During the time that Persia conquered Southwest Asia they were under rule of Cyrus The Great. ● Cyrus accomplished a lot during his reign. He united two tribes, the Medes and the Persians. He did this to rebel against his grandfather, king of the Medes Empire. ● Cyrus was liked by his people because he tolerated different cultures and customs. This was a popular idea amongst people. Therefore Persia attracted other people and increased the size of it’s empire. Achaemenid (550-530 B.C.) ● The Achaemenid Empire, or the First Persian Empire, rose to power in the 6th century led by Cyrus the Great. Tj e TheThe the ● Before Achaemenids, the Median confederation (Medes) resided in what is currently Iran. ● In order to gain the land and power, Cyprus the Great led his military into the Assyrian Empire using their cavalry weapons (paltas, few chariots, javelins, knives, and armor), and their great war tactics (three distinct services: chariots, horse and foot) with high numbers of troops to outflank and surround their adversary. Parthian (Arsacid Empire) • The Parni nomads settled in Parthia and built a small independent kingdom. • After, they rose to power under King Mithradates II. • The Parthian empire occupied all of modern Iran, Iraq and Armenia, parts of Turkey, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and territories in Pakistan, Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Palestine (briefly.) Sassanid ● The Sassanids took over in 224 C.E. ● They superseded the Parthians. ● They Sassanids brought back Achaemenid tactics and brought revival of Persian culture. ● In order to gain the land and power, the Sassanids took over Ctesiphon and this ended the rule of the Parthians. • • • • The Qin Dynasty was the first unified, multinational and power centralized state in Chinese History. They came after the Zhou dynasty. The Qin influenced the ways of the following dynasties. The first emperor of China, Yingzheng Emperor Qin Shi Huang, ruled during this time. He is described as a tyrant even though he made great contributions and adjustments for East Asia. He established the constructuction of the Great Wall of China. He began the line of Imperial Dynasties of China. However he burned many Confucian scholars alive along with their books. He and his son were the only people to ever rule during the Qin’s reign. The Qin did not make it past 20 years of ruling. East Asia: Qin • After the Qin dynasty fell apart two peasant leaders, Liu Bang and Xiang Yu, struggled with determining who would take on the role of ruling a new dynasty. • They eventually went against each other and Liu Bang defeated Xiang Yu to become the first leader of the Han Dynasty. • The Han Dynasty retained much of the Qin’s structure. However, Confucian ideals were very much valued and appreciated. Confucian scholars gained prominent status as the core of the civil service. East Asia: Han South Asia: Maurya ● First empire to provide single government for almost all of india ● Founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 326 bce in northern India. ● His son Bindusara and grandson Ashoka helped expand empire through conquest ● The last Mauryan ruler was killed in 183 bce by a general who established a dynasty (sunga) South Asia: Gupta ● Ruled most of north india in the common era (320-550ce) ● Expanded territory through war and marriage; also forced many rulers to submit to their power ● Empire succumbed completely in 550 ce when control of Bengal was lost. Mediterranean: Phoenicia and its colonies • Gained independence 1100 bce after the collapse of the Hittite empire • Influenced western culture through Carthage • Assyrians captured Phoenicians cities in 842 and were controlled by then until 612 bce • Eventually became a part of the Persian empire created by King Cyrus 1 (Cyrus the Great); prospered and maintained reputation as great sailors/shipbuilders Mediterranean: Greek city-states and colonies • Came under Greco-Macedonian rule (alexander the great) when Tyre was captured in 332 bce • 64 bce: Roman general Pompey the Great made Phoenicia part of the Roman province Syria; eventually fell to Arab Muslim invaders in 600’s ad • Alexander the Great Mediterranean: Hellenistic and Roman Empires • Empire extended from Greece to India • Hellenistic age: 323 bce (alexanders death)-146 bce • Roman’s took control of Greece and Macedonia in the 140’s bc • Greek culture spread throughout both empires • Roman empire divided in 395 as; west Roman empire consider in 476 ad; Roman empire survived as Byzantine empire until 1453 (fell to Ottoman empire) Mesoamerica: Maya City States • It was establish in 600 B.C (Tikal develops in 100 BC) • The Mayans didn’t take over land • They built upon their civilization Mesoamerica: Teotihuacan • It was establish in 100 BC but began to rise to power in 200 BC • It was used as an urban centerNo one knows who built this city but the Atecs later used the “Lost City.”yanmar-2328.ht Andean South America: Moche ● The Moche civilization flourished along the northern coast of ancient Peru, in 1 CE ● They took over surrounding territories (close with the Nazca) to become wealthy Chicago Style Works Cited Bunson, Margaret R., and Stephen M. Bunson. "Teotihuacán." Encyclopedia of Ancient Mesoamerica. New York: Facts On File, Inc., 1996. Ancient and Medieval History Online. Facts On File, Inc. http://www.fofweb.com/activelink2.asp? ItemID=WE49&iPin=MES1157&SingleRecord=True (accessed October 14, 2014). "Achaemenid Empire, Cyrus the Great, Darius the Great, Xerxes the Great - Crystalinks." Achaemenid Empire, Cyrus the Great, Darius the Great, Xerxes the Great - Crystalinks. http://www.crystalinks.com/Achaemenid_Empire.html- (accessed October 15, 2014). "No title." No title. http://persianempire.info/MILITARY.htm (accessed October 14, 2014). "History of Iran: Parthian Empire." History of Iran: Parthian Empire. http://www.iranchamber.com/history/parthians/parthians.php (accessed October 15, 2014). "History of Iran: Sassanid Empire." History of Iran: Sassanid Empire. http://www.iranchamber.com/history/sassanids/sassanids.php (accessed October 13, 2014). "Indus Valley Chronology." Indus Valley Chronology. http://www.imninalu.net/IndusValley.htm (accessed October 13, 2014).