* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Units at a- Glance
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
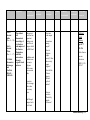
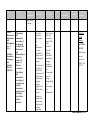
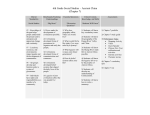
Units Standards Unit 1: The student will Pre-History demonstrate and the knowledge of Emergence the earliest of Civilizations human (Sept. 7 – 24) societies and the processes A. that led to the Beginnings of emergence of Human agricultural Society and societies Early around the Civilizations, world. to 1,000 B.C. Unit 2: Ancient Middle East (Mesopotami a, Sumerian, High School ELL Level 3 World History Units at a- Glance Standards Essential Reading Gramm Questions Strategies ar Paraphrased Historical Information helps us understand the past, present, and future. Farming, inventions, and new ideas changed the way people The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major characteristics of civilization and the process of its emergence. lived. The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major Not every culture changes into civilizations. How did farming change the way humans lived together? Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources ELL text World History, pp. 14-24 How do humans use what the environment has? Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 How do inventions change the way people live together? What is culture? What are the features of civilization? ELL text World History, World History – 1 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Assyrians, Persians, Phoenicians, & Israelites) (Sept. 27 – Oct. 15) A. Beginnings of Human Society and Early Civilizations, to 1,000 B.C. of B.C. characteristics of civilization and the process of its emergence. When people learned to make wild animals follow their directions, it gave humans food close to where they lived. Taking wild seeds and planting them, gave humans food close to where they lived. Ancient civilizations gave humans knowledge we still use today. Essential Questions Reading Strategies How does invention and development change human society? (domesticatio n) What contributions did ancient civilizations bring to the world? What types of physical features allow for food, work, and transportation ? (exploration) Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources pp. 27-38, 52-66 Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 Where people live and how people survive changes with the kinds of land, water, and climate are near them. World History – 2 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Unit 3: Ancient Africa (Egypt, Mali, Ghana, & Songhai) (Oct. 18 – Nov. 4/5) A. Beginnings of Human Society and Early Civilizations, to 1,000 B.C. B. World Civilizations and Religions, 1,000 B.C. 500 A.D. The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient African civilizations. The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major characteristics of civilization and the process of its emergence Trade was very important ancient African civilizations. Ancient African civilizations changed with differences in climate, water, and land. Religions with one God came to Africa. Essential Questions Reading Strategies What impact did trade have during 1000 B.C. and A.D. 500? What impact does the introduction of a new religion have on a civilization? What makes culture? What are aspects of culture? What sets one culture apart from another? What types of physical features and social developments allow for food, work, and transportation ? (exploration) Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources ELL text World History, pp. 40-50, 344-350 Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 World History World History – 3 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Unit 4: Ancient India (Nov. 8 – 30) Unit 5: Ancient China (Dec. 1 – 17) E. Global Encounters, Exchanges, and Conflicts, 500 A.D – 1,500 A.D. The student will demonstrate knowledge of civilizations and empires of the Eastern Hemisphere and their interactions through regional trade patterns. The ancient world had an important trading route from Asia to Europe called the Silk Road. Buddhism and Hinduism are two major religions which came from ancient India. Dynasties grow stronger and weaker over many years. The Mongol Empire had a lot of land. Essential Questions Reading Strategies How does trade impact the interactions among people? How do religions impact society? How does society impact religion? Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources ELL text World History, pp. 68-77. 225-226 Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-.13023828-7 How did the Chinese dynasty follow a cyclical pattern? How are societies affected by outside influences? World History – 4 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Essential Questions Reading Strategies Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources World History – 5 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Unit 6: Ancient Greece (Jan. 3 – 28) E. World Civilizations And Religions, 1,000 – 500 A.D. The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greek civilization and its influence throughout Eurasia, Africa and the Mediterranean. Greek culture went to many places. Many people still use Greek ideas and inventions today. Greece culture grew in many places by fighting and trade. Greece created a new kind of government. Mountains and seas in Greece made it easier to have strong cities than one large country. Essential Questions Reading Strategies Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources How did geography influence Greek society? ELL text How do societies influence their own types of governments? Globe Fearon World History, pp. 86-108 Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 How did trade and warfare influence the spread of Greek culture? How did the Greeks impact their physical environment? Where can Greek culture be seen outside of Greece? What caused the creation of city-states? World History – 6 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Unit 7: Ancient Rome (Feb. 1 – 25) B. World Civilizations and Religions, 1,000 B.C. 500 A.D. Unit 8: Americas (Feb. 28 – Mar. 11) E. Global Encounters, Exchanges, and The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 500 BC to 500 AD and its influence in relation to other contemporary civilizations. The student will demonstrate knowledge of complex societies and civilizations in the Americas. Rome borrowed and changed ideas from other civilizations. The strong Roman army made them the powerful dominance in the region. Rome changed it’s government from a republic to an empire. Ideas from the Roman Era continued in later societies. MesoAmerican civilizations had many original discoveries in science. There were Essential Questions Reading Strategies How did other societies influence the Romans? Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources ELL text World History, pp. 110-130 How did Rome expand and extend its influence? Why did Roman governments fail? What contributions did Rome give to the world? Globe Fearon How does architecture reflect a culture? ELL text How is society organized? pp. 78-82 How does Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 World History, 229-233 Globe Fearon World History – 7 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased class systems within MesoAmerican societies. Conflicts, 500 A.D – 1,500 A.D. Essential Questions Reading Strategies Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources geography impact society? Pearson Education How did the Crusades affect society? ELL text ISBN 0-13023828-7 Land, water, and climate in Central America were important in the growth oof MesoAmerican societies. Unit 9: Middle Ages (Mar. 14 – Apr. 8) E. Global Encounters, Exchanges, and Conflicts, 500 A.D. – 1,500 A.D. The student will demonstrate knowledge of the interactions between Christendom and the Islamic world, 750 to 1,500 A.D. The student will demonstrate knowledge of social, economic, and In the late Middle Ages, Europeans traded with Asia, Africa, North America, and South America. Fighting between Christians and Muslims changed society, economy, and the way What role did Constantinople play in Medieval Europe’s society? How are religious conflicts manifested? World History, pp. 134-143 Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 World History – 8 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased political changes and cultural achievements in the late medieval period. Unit 9: Middle Ages (Mar. 14 – Apr. 8) E. Global Encounters, Exchanges, and Conflicts, 500 A.D – 1,500 A.D. Essential Questions Reading Strategies people looked at their world. How do religious ideas influence regional development? Feudalism, a political and social system was the strongest force Medieval life. What is the purpose of government? The Catholic Church was important in all areas of Medieval life. During the Middle Ages, European cities grew, making it possible to have and a middle class. Disease comes to What conflicts exist between the secular and religious worlds? What is the role of the ‘rule of law ‘in society? Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources ELL text World History, pp. 146-178 Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 How does disease affect society? How has ‘learning’ changed over time? World History – 9 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Essential Questions Reading Strategies New ideas change the ways people live. Why do some ideas and innovations remain while others diminish? Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources many places in Europe. Unit 10: Renaissance, Exploration, and Reformation (Apr. 11 – May 6) E. Global Encounters, Exchanges, and Conflicts, 500 A.D – 1,500 A.D. The student will demonstrate knowledge of development leading to the Renaissance and Reformation in Europe in terms of its impact on Western civilization. The student will demonstrate knowledge of economic and political interactions among peoples of Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The Renaissance was very important to changes in art and thought in Europe. The division of the Catholic Church into Protestants and Catholics (the Reformation) changed people’s religious and political lives Europe. How did different individuals contribute to changes during the Renaissance and Reformation? ELL text World History, pp. 181-212, 215-224 Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 How did Europe change during the Renaissance and Reformation? Changes in business and money begin religious and thinking changes in World History – 10 Units Standards Standards Paraphrased Essential Questions Reading Strategies Gramm ar Formative Assessments Summative Assessment s Text(s) and Resources Europe. Unit 11: Revolutions (May 9 – June 8) G. Age of Empires and Revolutions, 1,640 – 1,920 A.D. The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, philosophical, economic and religious changes during the 17th and 18th Centuries. There are many kinds of revolutions that change in the world. Large business companies were very important in Europe and the rest of the world. Different countries are more or less interested in finding out about places far away or making their countries larger. What is a revolution? How does trade positively and negatively affect cultures? How did the French Revolution change political thought? ELL text World History, pp. 250-299, 332-342 Globe Fearon Pearson Education ISBN 0-13023828-7 Trying to have more than other countries, can start trouble. World History – 11 World History – 12