* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Date: Period:____ Study Guide for Plate Tectonics Key 1
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
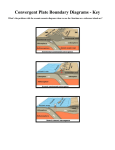
Name:__________________________ Date:______________ Period:____ Study Guide for Plate Tectonics Key 1. What is the theory of continental drift? Who was founded the theory? Theory: the theory the continents were once a supercontinent that broke up into plate and drifted apart. Founded by Alfred Wegener. 2. List 4 examples of evidence to support continental drift. Landforms, Climate, Fossils from plants and animals, & sea-floor spreading 3. Explain sea-floor spreading. Where does this occur? The process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises towards the surface and solidifies. It occurs at divergent plate boundaries & the mid-ocean ridge. 4. List the physical layers of the earth. Be able to describe their composition and whether they are a liquid, solid, or gas. Composition Layers: Crust, Mantle, & Core Physical Layers: Crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core, & inner core See matrix for all composition and all layers are solid except outer core is a liquid (The difference between density of the crust and the core is that the core contains more iron, thus making it denser) 5. What is Pangaea? What is Laurasia? Gondwana? Pangaea-supercontinent from continental drift; Laurasia (top half of supercontinent once it broke into 2 parts; Gondwana- bottom half of supercontinent) 6. Describe the boundaries (convergent, divergent, & transform) Convergent-collides o Continental-Continental ~ collision creating mountains (ex: Himalayas) o Oceanic-Oceanic ~ denser plate subducts (creates island arcs) o Oceanic-Continental ~ oceanic plate subducts (creates volcanoes on land) Divergent- separates Transform-slide past one another 7. Convergent-collides & produces earthquakes o Continental-Continental ~ mountain ranges (ex: Himalayas) o Oceanic-Oceanic ~ creates island arcs o Oceanic-Continental ~ creates volcanoes on land Trenches always occur at subduction zones Divergent- Mid-Ocean Ridges & Seafloor Spreading; Volcanoes & Earthquakes Transform-Earthquakes 8. What is subduction? Where does it occur? Where do mountains form? Subduction- when one plate, the denser plate, slides up underneath another plate. It occurs at convergent boundaries that are continental-oceanic and oceanic-oceanic. Mountains are formed from convergent boundaries that are continental-continental. 9. What is magnetic reversal? What does it help support? Magnetic reversals are when the magnetic poles change places. It helps support seafloor spreading. 10. What are the three types of faults? Normal, Reverse, & Strike-Slip 11. What type of stress causes each type? Normal fault- stress by tension; Reverse fault- caused by compression; and strike-slip fault (not caused by either) 12. What is the relationship between a footwall and a hanging wall? Normal fault-the hanging wall moves downward Reverse fault- the handing wall moves upward 13. How do we map the interior of the earth? Seismic waves 14. Convergent Boundary Divergent Boundary Transform Boundary 15. A Convection Current is the continued heating & cooling of molten rocks that drives the movement of tectonic plates. It occurs in the asthenosphere.