* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Automotive Ignition Systems
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Phone connector (audio) wikipedia , lookup
Industrial and multiphase power plugs and sockets wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
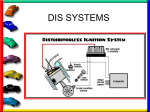
Automotive Ignition Systems Ignition System Purpose Create a high voltage spark Deliver the spark at correct time w St uf f W or ks .c o m Ignition Timing BTDC ATDC Engine RPM Engine Load Firing Order Retard Advance Firing Order Firing Order 1,3,4,2 1,2,5,4,3,2 1,5,6,3,4,2,7,8 Firing Order Ignition System Circuits Primary Circuit (Low Voltage) Ignition Switch Resistor Coil Primary Winding Ignition Module Pick-up Assembly Secondary Circuit (High Voltage) Coil Secondary Winding Coil Wire Distributor Cap & Rotor Plug Wires Spark Plugs Ignition Primary Circuit Battery Ignition Switch Resistor Coil Winding Ignition Module Pick-up Assembly Low voltage side Ignition Coils Step-up transformer Primary winding Secondary winding Uses electromagnetic induction to operate Magnetic field must be built up and then collapsed Ignition Coil High Voltage wire + Battery - ign module Primary Windings Secondary Windings Making & Breaking Fields Ignition Modules Old Systems Used Breaker Points Modules Contain a Switching Transistor Externally Mounted Distributor Mounted Ignition Pick-up Assemblies Can be mounted in one of five different locations: #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 Distributor Vibration Damper Flywheel Crankshaft Camshaft Distributor A mechanical timing device Drives off engine camshaft Can controls both primary and secondary circuits May contain advance units The Rotor at Work Rotates around to DISTRIBUTE voltage to each spark plug http://www.hows tuffworks.com/igni tion-system4.htm Ignition Secondary Circuit Coil Winding Coil Wire Distributor Cap & Rotor Spark Plug Wire Spark Plug Distributor Cap & Rotor Cap fits on top of the distributor housing Made of lexon plastic Has an index mark for proper installation Rotor fits on top of distributor shaft Also is indexed Spark Plug Wires Very high resistance wire 1000 ohms per inch Mostly insulation material Small conductor material Must follow firing order Spark Plug Placement Spark Plugs Shell w/threads Ceramic insulator Center electrode Side electrode Plug gap Heat range Plug designation Resistor Plugs Heat Rages of Plugs The difference between a "hot" and a "cold" spark plug is in the shape of the ceramic tip. The difference between a "hot" and a "cold" spark plug is in the shape of the ceramtip. The carmaker will select the right-temperature plug for each car. Some cars with high-performance engines naturally generate more heat, so they need colder plugs. If the spark plug gets too hot, it could ignite the fuel before the spark fires; so it is important to stick with the right type of plug for your car. Spark Plugs tell a story Normal Over Heating Worn Carbon Lead Erossion Fuel/Additive Deposits Insulator Breakage Lead Fouled Lead Fouled Minor Melting Oil Old Breaker Point Ignition Used 1920’s - 1974 mechanical switch in distributor build-up - collapse coil magnetic field Points wear out Must be replaced each year Breaker Point (dwell angle) Breaker Point Parts Making & Collapsing field Electronic Ignition with Distributor (HEI) 1970’s Transistor in ignition module turns coil on/ off Module mounted externally or in distributor Pick-up in distributor High Energy Ignition (HEI) Trigger Wheel No Points Rotating Reluctor Wheel Fewer Tune-Ups More Efficient Optical Trigger (Chrysler) Photo Electric Sensor (Photo = Light) CKPS (crankshaft position sensor) Fewer Parts No Points No Distributor No Rotor Computer Controlled More Efficient Crank Trigger Wheel Direct Ignition No Distributor One Coil for Two Cylinders Waste Spark System One Plug Fires Backwards Wasted Spark 1st plug fires forward 2nd fires backwards Sister cylinders Direct Ignition Coil Over Business End of the Ignition System Size Reach Heat Range Spark.Air Gap Ignition System Maintenance Replace Spark Plugs every 30,000mi/36mo Inspect Cap and Rotor (replace if necessary) Inspect Spark Plug wires (replace if necessary) Check Firing Order Check Ignition Timing (if necessary) Timing Engine Warm At Idle Defeat Advance #1 Plug wire