* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Ignition System
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Phone connector (audio) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
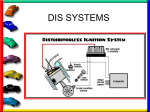
Spark Plugs Chapter 1 Outline 4 Types of Ignition System Structurally, ignition system can be classified into the following three types. Contact Ignition Type 1 Battery 2 Ignition switch 3 Ignition coil 4 Breaker point 5 Distributor 6 Rotor 7 Spark plug 1 Battery This system generates high voltage by cutting off the current with transistors in the igniter. This system can provide stable high voltage. 2 Ignition switch 3 Coil with an igniter Demerit 4 Signal generator The ignition timing is controlled by the signal generator in the distributor, so there are limits to fine control. 5 Distributor 6 Rotor 7 Spark plug (Ordinary Ignition Type) In this system, the current (primary current) flowing to the ignition coil from the battery is cut off at the mechanical contacts (breaker points) in the distributer to generate high voltage. Demerit Since these are mechanical contacts, sparks can fly between the contacts or the voltage drops at low speed. Also, sometimes current does not flow adequately due to soiling of the contact surface. Transistor Ignition Type Electronic Spark Advance (ESA, DLI) Electronic ignition type (ESA:Electronic Spark Advance, DLI:Distributorless Ignition) The ignition timing and dwell angle are controlled by microcomputer, which sends the ignition signals to the igniter, where the transistors inside the igniter cut off the current and generate high voltage. This makes more precise control possible and is the current mainstream ignition system. Distributor IGt Engine speed .NE Crankshaft position detection .G Ignition timing control Sensors Air flow sensor Water temperature sensor Air conditioner signal etc Igniter ECU Dwell angle control Constant-current control Ignition signal Ignition Dwell angle reduction IGf Ignition monitor signal 5 Comprehensive Test From the following statements about ignition system, select the incorrect one. 1 Both gasoline engines and diesel engines require spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture. 2 The ignition timing is adjusted according to changes in the engine speed and load. 3 The air-fuel mixture for gasoline engines is the proportion of air and gasoline by weight and about 15:1 is called the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. 4 The spark voltage for spark plugs is generated when the primary current through the igniter is cut off. 5 4-cycle engines ignite and combust each cylinder one time for two rotations for the engine crankshaft. Answer on next page 08