* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Asteroids, Meteors, Comets
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Comet Hale–Bopp wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Chelyabinsk meteor wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Tunguska event wikipedia , lookup
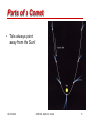
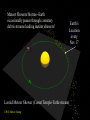
Ch 8--Asteroids, Meteors, Comets 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 1 What do you think? • Are the asteroids a planet that was somehow destroyed? • How far apart are the asteroids on average? • Why do comets have tails? • In which direction does a comet tail point? • What is a shooting star? 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 2 Early Solar System • From studying cratering on the Moon and the planets – First half-billion year had many collisions between planetesimals – More recently the collisions are much less frequent, but do occur! 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 3 Asteroids • Asteroids: – remnant planetesimals • also known as “minor planets” – mainly concentrated in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter--about 10 million miles average separation – Mostly stony or metallic in composition 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 4 Asteroids • 1801--Piazza discovers Ceres--the first asteroid 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 5 Asteroids--Origins • A destroyed planet? – Probably not • Jupiter’s gravity creates “resonances” which create bands of stable orbits and gaps of unstable orbits – Kirkwood gaps discovered 1867 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 6 Asteroids outside the belt • Gravitational perturbations eject comets from the belt into elliptical orbits – Some approach the inner planets – “Apollo” asteroids cross the Earth’s orbit • Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) • Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs) • Potentially Hazardous Objects (PHOs) 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 7 Comets • Comets--best thought of as “dirty snowballs” orbiting the Sun which evaporate due to solar heating 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 8 Comets Origins • Primordial gas, dust, and ice frozen in clumps at the outer limits of the solar system – Kuiper belt--out to 500 AU – Oort Cloud--50,000 AU • Occasionally perturbed into elliptical orbits approaching the Sun 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 9 Parts of a Comet • Coma--spherical cloud of vaporized gas around the frozen nucleus • Tails--trail of debris – dust tail--dust particles blown away by solar radiation – ion tail--ions carried away by solar wind 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 10 Parts of a Comet • Tails always point away from the Sun! 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 11 Comets Demise • Comets eventually – – – – breakup into smaller fragments (Comet West below) evaporate collide with the sun collide with other planets 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 12 Comets Demise 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 13 Comets Demise 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 14 Meteoroids, Meteors, Meteorites • Meteoroids--small rocky or metallic particles throughout the solar system • Meteors--upon entering Earth’s atmosphere, friction causes heat and disintegration--shooting stars • Meteorites--remnants surviving on the ground 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 15 Meteor Showers/Storms--Earth occasionally passes through cometary debris streams leading meteor showers! Earth’s Location every Nov 17 Leonid Meteor Shower (Comet Temple-Tuttle stream) UWO Meteor Group 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 16 Meteorites • Meteorites--remnants surviving on the ground – Mostly remnants of asteroids (to have survived entry into Earth’s atmosphere) • Stony meteorites • Iron meteorites – Show melting and wearing patterns from processing in asteroids – Carbonaceous Chondrites show no melting • may be primordial components of solar system • contain organic material! 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 17 Dino Killers? • Evidence for large impact 65 Million years ago • Alvarez theory of K-T boundary • Impact crater evidence found off north shore Yucatan at Chixulub 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 18 More Recent Events • Meteor Crater – 30,000 BCE – 1.2 km crater – 30 m meteor • Tunguska 1908 – ~ 1/2 km size – 2200 sq km area • 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll Peekskill 1993 – ~1m size 19 Planetary Defense? Easy to study; expensive to carry out! 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 20 What do you think? • Are the asteroids a planet that was somehow destroyed? – No, the gravitational pull of Jupiter prevented the planetesimal in the asteroid belt to coalesce into planet • How far apart are the asteroids on average? – The distance between asteroids averages about 10 million miles • Why do comets have tails? – Gas and dust evaporated from the comet nucleus are blow away by the solar wind and solar radiation pressure, respectively • In which direction does a comet tail point? – Gas tails point directly away from the Sun; Dust tails point indirectly away from the sun in arcs • What is a shooting star? – A piece of space debris plunging white hot into the Earth’s atmosphere--a meteor, not a star 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 21 Questions for Thought • Explain the origins of comets and describe the various features seen when near the Sun. 03 Oct 2000 ASTR103, GMU, Dr. Correll 22