* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
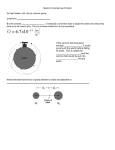
Force A force is a push or a pull. Force is a vector quantity and can be shown with magnitude and direction. The SI unit of force is the newton, (N). The net force is all of the forces acting on an object. Ex. A kicked soccer ball has the force of the kick, force of gravity, and the force of the grass/or air rubbing on the outside of the ball. These are all unbalanced forces and cause the ball to change its velocity. When the soccer ball comes to a stop on the ground the force of gravity pulling down and the force of the ground pushing up on the ball are balanced. Balanced forces do not change the ball’s velocity. Friction is a force that acts in the opposite direction of the motion of objects. There are four types of friction: Static friction – friction that acts on objects that are not moving. Sliding Friction – a force that occurs when two solid surfaces slide over each other. Rolling Friction – occurs when an object rolls across a surface. Fluid Friction – occurs when a solid object moves through a fluid. Gravity is a force that pulls objects toward each other. It increases with greater mass and decreases with distance. Mass is how much matter is in an object. Ex. A bowling ball has more mass than a soccer ball. Weight is the force of gravity pulling on a mass. A bowling ball weighs more on Earth than it does on the moon because the moon has less of a gravitational force than Earth. Weight = mass X acceleration due to gravity An object is in free fall if it only has the force of gravity acting on it. In a vacuum, where there is no air at all, objects fall at the same rate of acceleration. But on Earth falling objects encounter air resistance, a type of fluid friction. Ex. An open parachute has more air resistance acting on it than a closed parachute. On Earth the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2. Gravity pulls objects toward the center of Earth in the same way it pulls a dropped object and a thrown object, also called a projectile. Matter can be affected by elastic forces. If it is squeezed it’s called compression. If matter is stretched it’s called tension. Ex. A slinky can be pulled apart – tension and squeezed together – compression.