* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
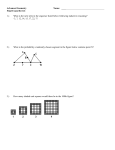
Geometry Label each figure with the information given. 1. 2. PR = 7 = 105° RO = 4 3. AE = CD 4. RU = US VU = TU RV = ST Use the markings on the drawings to find the missing information. 5. 6. _?_ _?_ 7. WX = _?_ ZY = _?_ = _?_ _?_ _?_ AE = _?_ In the diagram, is a right angle. Name the figures described. 8. Two congruent 9. supplementary angles Two noncongruent supplementary angles 10. Two acute vertical angles 11. Two obtuse vertical angles Draw and carefully label the figure described. || and ^ 12. Trapezoid ABCD with . 13. Scalene ∆MNP with MP = 3, PN = 5, and MN = 7. 14. Hexagon RSTUVW with diagonal 15. Isosceles right ∆XYZ with 16. Trapezoid JKLM with and the non-parallel sides. midpoint of and Q be the midpoint of . Draw PQ. parallel to sides and . . Let P be the Use your ruler and protractor to analyze the quadrilaterals below to discover additional attributes (beyond the definition) about each. Here is a parallelogram. • What do you know about its sides? • What do you know about its interior angles? • Draw the two diagonals. What do you know about them? Here is a rhombus. • What do you know about its sides? • What do you know about its interior angles? • Draw the two diagonals. What do you know about them? Here is a rectangle. • What do you know about its sides? • What do you know about its interior angles? • Draw the two diagonals. What do you know about them? Here is a square. • What do you know about its sides? • What do you know about its interior angles? • Draw the two diagonals. What do you know about them? Here is a trapezoid. • What do you know about its sides? • What do you know about its interior angles? • Draw the two diagonals. What do you know about them? Here is an isosceles trapezoid. • What do you know about its sides? • What do you know about its interior angles? • Draw the two diagonals. What do you know about them? Here is a kite. • What do you know about its sides? • What do you know about its interior angles? • Draw the two diagonals. What do you know about them? Additional Practice 3 (for use after Investigation 9) Calculate each lettered angle measure and explain your reasoning for each response. a. b. c. Geometry Unit Vocabulary space: the set of all points. collinear points: points that lie on the same line. coplanar points: points that lie on the same plane. line segment: that part of a line between and including two points. ray: part of a line containing a point and all the points on the line to one side of the given point. angle: two rays that share a common endpoint. congruent segments: segments that have equal lengths. congruent angles: angles that have equal measures. right angle: angle whose measures is 90° acute angle: angle whose measure is less than 90° obtuse angle: angle whose measure is greater than 90° angle bisector: ray that divides an angle into two equal parts midpoint: point that divides line segment into two equal parts parallel lines: coplanar lines that do not intersect perpendicular lines: lines that meet at right (90°) angles complementary angles: 2 angles whose sum is 90° supplementary angles: 2 angles whose sum is 180° vertical angles: 2 non-adjacent angles formed by intersecting lines corresponding angles: angles on the same side of the transversal and same side of the coplanar lines alternate interior angles: angles on either side of the transversal and in between the coplanar lines polygon: closed figure formed by line segments congruent polygons: polygons that have the same size and shape diagonal: line segment joining 2 non-adjacent vertices of a polygon equilateral polygon: polygon with all sides equal equiangular polygon: polygon with all angles equal regular polygon: equilateral, equiangular polygon right triangle: triangle with one 90° angle acute triangle: triangle with all angles acute obtuse triangle: triangle with one obtuse angle scalene triangle: triangle with no sides equal isosceles triangle: triangle with two sides equal equilateral triangle: triangle with all sides equal trapezoid: quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides parallelogram: quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides rhombus: equilateral parallelogram (or quadrilateral) rectangle: equiangular parallelogram (or quadrilateral) square: (1) regular quadrilateral, or (2) equiangular rhombus, or (3) equilateral rectangle kite: quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent congruent sides Other vocabulary that can be introduced: coplanar lines: lines that lie on the same plane skew lines: non-coplanar lines that do not intersect linear pair: 2 adjacent angles that form a line vertex angle: angle between the two equal sides of an isosceles triangle base angles: angles opposite the two equal sides of an isosceles triangle median: line segment joining vertex with midpoint of opposite side in a triangle midsegment: line segment joining two midpoints in a polygon altitude: line segment from vertex perpendicular to opposite side in a triangle height: (1) length of an altitude in a triangle (2) length of perpendicular segment connecting parallel sides in a quadrilateral segment bisector: line that passes through midpoint of a segment perpendicular bisector of a segment: line that divides segment into two equal parts and is perpendicular to the segment