* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Trans
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
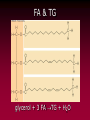
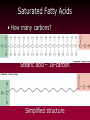
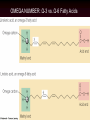
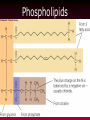
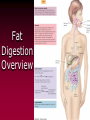
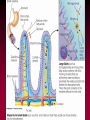
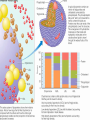
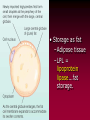
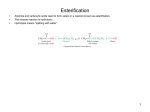
The Lipids Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols Lipids • Triglycerides (TG) –Fats and oils • Phospholipids • Sterols Fatty Acids (FA) & TG • glycerol-a sugar alcohol, backbone of a FA! • REM: they have carbon (C), so they are organic! FA & TG glycerol + 3 FA TG + H2O Condensation of Glycerol & Fatty Acids to Form a Triglyceride Fatty Acids –Length (size matters) –Saturated vs. unsaturated • Acetic Acid (most simple) Saturated Fatty Acids • How many carbons? Stearic acid – 18-carbon Simplified structure Fatty Acids • Point of saturation (where?) • Degree of saturation (how much?) –Saturated fatty acid •Monounsaturated •Polyunsaturated An impossible chemical structure: Why? Oleic acid – 18-carbon, monounsaturated Linoleic acid – 18-carbon, polyunsaturated OMEGA NUMBER: Ω-3 vs. Ω-6 Fatty Acids TG: Why Does Saturation Matter? • Unsaturation effects: –Firmness –Stability •Oxidation –Antioxidants Triglycerides:What about “hydrogenated oils?” –Hydrogenation-hydrogen added to mono- or polyunsaturated fats to make them solid by reducing the number of double bonds (C=C). –Cis vs. trans-fatty acids Hydrogenation Cis- and Trans-Fatty Acids Compared So what? It’s a nice picture. Trans fats are bad!!! • In the body trans fats behave like saturated fats! Why? • They contribute to higher LDL cholesterol and lower levels of "good" HDL cholesterol = heart disease. Phospholipids Phospholipids (PL) • Phospholipids in foods • Roles of PL –Plasma membrane –Emulsifiers (help oil and water exist together) Membrane Structure PL Hydrophobic tail vs. hydrophilic head: more on this later. Sterols Sterols • Roles of sterols: Good –Bile acids –Sex hormones –Adrenal hormones –Vitamin D • Roles of sterols: Bad -Atherosclerosis-hardening of arteries. Fat Digestion Yummy...or not. Fat Digestion • Hydrolysis –Triglycerides monoglycerides, fatty acids, glycerol Fat Digestion Fat Digestion • Mouth –Melting –Lingual lipase Fat Digestion • Stomach –Churning and mixing –Gastric lipase Fat Digestion • Small intestine –CCK-hormone which signals bile release! •Bile emulsifies fats. Fat Digestion Fat Digestion Fat Digestion • Small intestine –Pancreatic lipases –Intestinal lipases Fat Digestion Overview Fat Digestion • Enterohepatic circulation • Note how fiber helps remove excess cholesterol!! Lipoproteins and health Factors that lower LDL and raise HDL – Weight control – Replace saturated fat with monounsaturated fat and polyunsaturated fat in the diet – Soluble fibers – Phytochemicals – Moderate alcohol consumption – Physical activity (biggest helper) • Genes influence lipoprotein activity. Roles of Triglycerides • Fat stores –Energy –Protection –Insulation Essential Fatty Acids Fat Metabolism • Storage as fat –Adipose tissue –LPL = lipoprotein lipase...fat storage. Lipid Metabolism • Using fat for energy – Hormone-sensitive lipase...triglyceride release. – Provides very little glucose...problem during fasting? Health Effects of Lipids • Blood lipid profile • Heart disease • Risks from saturated fats Health Effects of Lipids:US Diet Dietary Cholesterol Health Effects of Lipids • Benefits:monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats • Cancer • Obesity Health Effects and Recommended Intakes of Lipids • Recommended Intakes of Fat – DRI: 20-35% of energy intake (400-700 kcalories of a 2,000-kcal diet). – FDA recommends 10% of energy intake from s • Linoleic acid AI 5-10% of energy intake Linolenic acid AI 0.6-1.2% of energy intake – aturated, 30% of energy intake total fat Health Effects and Recommended Intakes of Lipids – Daily Values • 65 g fat based on 30% of 2000-kcal diet • 20 g sat. fat based on 10% of 2000-kcal diet • 300 mg cholesterol – USDA Food Guide considers saturated fats discretionary kcalories. – Too little fat can be detrimental to health. Health Effects and Recommended Intakes of Lipids • Health Effects of Lipids – Blood lipid profile • Reveals concentrations of lipids in the blood • Desirable levels – Total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL – LDL cholesterol < 100 mg/dL – HDL cholesterol ≥ 60 mg/dL – Triglycerides < 150 mg/dL Cutting Fat Cuts kCalories and Saturated Fat Guidelines to Groceries • Milk and milk products • Vegetables, fruits, and grains • Invisible fat High-Fat Foods • Changing guidelines for fat intake High-Fat Foods • Cook with olive oil • Nibble on nuts • Feast on fish –But beware of mercury? High-Fat Foods • Mediterranean diet?