* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
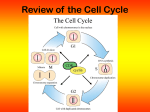
Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Skills Worksheet CH10.1 Active Reading Section: Cell Reproduction Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for RNA and protein. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of proteins needed by the cell. As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide, the DNA and the proteins associated with the DNA coil into a structure called a chromosome. Before the DNA coils up, however, the DNA is copied. The two exact copies of DNA that make up each chromosome are called chromatids. In the chromatids, the DNA is very condensed. The two chromatids, which become separated during cell division and are placed into each new cell, ensure that each new cell has the same genetic information as the original cell. SKILL: READING EFFECTIVELY Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1. How are genes and DNA related? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What occurs to a DNA strand as its genes are being used? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. How are chromatids and chromosomes related? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ An analogy is a comparison. In the space provided, write the letter of the term that best completes the analogy. _____ 4. A train is to cars as a molecule of DNA is to a. chromatids. b. genes. c. proteins. d. RNA. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 9 Cell Growth and Division Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Skills Worksheet CH10.2 Active Reading Section: Mitosis Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. During its lifetime, a cell goes through a repeating sequence of cellular growth and division. This repeating sequence is called the cell cycle. A cell spends 90 percent of its time in the first three phases of the cycle, which are collectively called interphase. A cell will enter the last two phases of the cell cycle only if it is about to divide. The five phases of the cell cycle are as follows: First gap (G1) phase: During the G1 phase, a cell grows rapidly and carries out its routine functions. This phase occupies the major portion of the cell’s life in most organisms. Synthesis (S) phase: A cell’s DNA is copied during this phase. At the end of this phase, each individual chromosome consists of two sister chromatids attached at the centromere. Second gap (G2) phase: In the G2 phase, preparations are made for the nucleus to divide. Mitochondria and other organelles replicate. Hollow protein fibers called microtubules are assembled. The microtubules are used to move the sister chromatids during mitosis. Mitosis: The process during cell division in which the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei is called mitosis, each with a complete set of the cell’s chromosomes. Cytokinesis: The process during cell division in which the cytoplasm divides is called cytokinesis. In this process, each daughter cell receives about half of the original organelles in a cell. SKILL: READING EFFECTIVELY Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1. Identify and define the two Key Terms in the first paragraph of this passage. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. A cell viewed under a high-powered microscope appears to be in the fourth phase of the cell cycle. What does this indicate about the cell? _______________________________________________________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 10 Cell Growth and Division Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Active Reading continued SKILL: SEQUENCING INFORMATION Match each statement with the phase of the cell cycle it describes. Write the letter of the correct phase in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once. _____ 3. The nucleus divides. _____ 4. It makes up a major portion of most cells’ lives. _____ 5. The cytoplasm divides. a. b. c. d. e. first gap phase synthesis phase second gap phase mitosis cytokinesis _____ 6. The mitochondria replicate. _____ 7. The cell grows rapidly. _____ 8. Two identical nuclei are produced. _____ 9. DNA is copied. _____ 10. Microtubules are assembled. _____ 11. Sister chromatids form and become attached at the centromere. _____ 12. The cell carries out its routine functions. _____ 13. Microtubules move sister chromatids. Read the question, and write your answer in the space provided. 14. How are mitosis and cytokinesis alike? How do they differ? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ An analogy is a comparison. In the space provided, write the letter of the term that best completes the analogy. _____ 15. G2 phase is to mitochondria as S phase is to a. chromatids. b. centromere. c. microtubules. d. DNA. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 11 Cell Growth and Division Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Skills Worksheet CH10.3 Active Reading Section: Regulation Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. The cell cycle has checkpoints. These are mechanisms the cell uses to make sure it is ready to go on to the next phase. There are three main checkpoints in the cell cycle. The first checkpoint comes during the first gap phase. It is called the G1 checkpoint. Its purpose is to check the cell and its surroundings before cell division begins. The cell needs to be large enough and healthy enough to undergo cell division. It needs to have adequate nutrients and oxygen to sustain the process. If conditions are not favorable, the cell goes into a resting phase. If conditions are favorable, the cell enters the synthesis phase. The second checkpoint comes during the second gap phase. It is called the G2 checkpoint. Its purpose is to ensure that the cell is ready for mitosis. As with the G1 checkpoint, the cell must still be large enough and healthy enough to continue cell division. The copied DNA must be identical to the original DNA. If there are mistakes in the copied DNA, enzymes correct the mistakes. If the cell is not large enough, the cell continues growing until it reaches the optimal size. When conditions are favorable, mitosis begins. The third checkpoint comes during metaphase in mitosis. It is called the mitosis checkpoint. Its purpose is to check that the genetic material will divide properly into the two daughter cells. During the mitosis checkpoint, the cell makes sure that all the chromosomes have lined up properly at the cell equator. It checks to make sure that each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle. If chromosomes need rearranging or attaching or reattaching to the spindle, the cell makes these adjustments. When conditions are favorable, mitosis continues. SKILL: READING EFFECTIVELY Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1. What is the general purpose of the checkpoints related to the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. Why are checkpoints important to the health of cells? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 12 Cell Growth and Division Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Active Reading continued 3. When does the G1 checkpoint occur? What does the cell check? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. What happens if a cell does not pass the G1 checkpoint? _______________________________________________________________ 5. What happens if a cell passes the G1 checkpoint? _______________________________________________________________ 6. When does the G2 checkpoint occur? What does the cell check? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 7. What happens if a cell does not pass the G2 checkpoint? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 8. What happens if a cell passes the G2 checkpoint? _______________________________________________________________ 9. When does the mitosis checkpoint occur? What does the cell check? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 10. What happens if a cell does not pass the mitosis checkpoint? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 11. What happens if a cell passes the mitosis checkpoint? _______________________________________________________________ Write the letter of the term that best answers the question. _____ 12. Which graphic could you use to best show the checkpoints in the cell cycle? a. line graph b. bar graph c. flowchart d. map Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 13 Cell Growth and Division