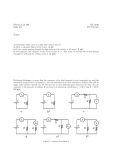
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name:
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Name: Lab Partner(s): Date lab performed: Dr. Julie J. Nazareth Physics 133L Section: Basic Circuits Follow the procedure as outlined in your lab manual. Part A: Series Circuit A-1: Connect the series circuit shown in figure 3 of your lab manual. Note what symbols are used to represent the light bulbs and the power supply in the figure, as well as the arrow showing the direction of conventional current flow. Question A-1a) What happens when you unscrew one of the light bulbs from its socket? Be specific and explain why it happened. (Replace the bulb when done.) Question A-1b) What happens if you increase the power supply voltage slightly? Question A-1c) What would happen if you were to unscrew the other light bulb? Connecting an ammeter: Make sure that you DO NOT change the voltage setting on the power supply. Simply unplug the banana plug from the positive terminal of the power supply to connect or reconnect the ammeter in the circuit. A-2: Connect the ammeter as shown in the left hand circuit drawing of figure 5. (Connect the ammeter in series BEFORE the first bulb to measure the current going into the first bulb, I1.) Draw both a schematic diagram and a sketch of the real circuit for the left hand series circuit. The schematic diagram must include all of the elements in your real circuit , + and – signs at the power supply symbol indicating the positive and negative sides of the circuit, an arrow indicating the direction of the conventional current, and the resistors (light bulbs) labeled as bulb 1 (or R1) and bulb 2 (or R2). Use resistor symbols to represent the light bulbs since we are only concerned with the bulb’s electrical resistance. Please keep bulb 1 and 2 consistent throughout the lab. Schematic diagram Real circuit Lab: Basic Circuits Updated 09/13/12 Data & Reporting score: Connect the ammeter as shown in the right hand circuit drawing of figure 5. (Connect the ammeter BETWEEN the two bulbs to measure the current going into the second bulb, I2.) Schematic diagram Real circuit Table 1: Current measurements for series circuit Current (bulb 1), I1 ( ) Current (bulb 2), I2 ( ) Relationship between I1 and I2 Connecting a voltmeter: Make sure that you DO NOT change the voltage setting on the power supply. Simply unplug the banana plug from the positive terminal of the power supply to connect or reconnect the voltmeter in the circuit. A-3: Connect the voltmeter as shown in the center circuit drawing of figure 7. Connect the voltmeter in parallel with the first bulb to measure the voltage across (from one side of the bulb to the other) the first light bulb, V1. Without changing the voltage on the power supply, connect the voltmeter in parallel with the second bulb only (left hand circuit drawing of figure 7) to measure the voltage, V2. Then, without changing the voltage on the power supply, connect the voltmeter across both bulbs (right hand circuit drawing of figure 7) to measure the voltage across the combination of light bulbs, V3. Table 2: Voltage measurements for series circuit Voltage (bulb 1), Voltage (bulb 2), Voltage (combination), V1 ( ) V2 ( ) V3 ( ) Relationship between V1 V2, and V3 Part B: Parallel Circuit B-1: Connect the parallel circuit shown in figure 8 of your lab manual. Question B-1a) What happens when you unscrew one of the light bulbs from its socket? Be specific and explain why it happened. (Replace the bulb when done.) Question B-1b) What happens if you increase the power supply voltage slightly? Question B-1c) What would happen if you were to unscrew the other light bulb? Lab: Basic Circuits Updated 09/13/12 For B-2 and B-3, DO NOT change the voltage setting on the power supply between the various circuit configurations. Simply unplug the banana plug from the positive terminal of the power supply to change your circuit. B-2: Connect the ammeter in your circuit as shown in figure 10. (Connect the ammeter in series between power supply and only one of the bulbs, the top bulb.) Measure the current through the top bulb, I1, and record the value in table 3. Draw both a schematic diagram and a sketch of the real circuit that you made. Ammeter reading of current through top bulb only Schematic diagram Real circuit Without changing the voltage on the power supply, reconnect the ammeter so it reads current through the bottom bulb only, I2. Draw both a schematic diagram and a sketch of the real circuit that you made. Ammeter reading of current through bottom bulb only Schematic diagram Real circuit Without changing the voltage on the power supply, reconnect the ammeter so it reads current through the combination of both bulbs, I3. Draw both a schematic diagram and a sketch of the real circuit that you made. Ammeter reading of current through combination of both bulbs Schematic diagram Real circuit Lab: Basic Circuits Updated 09/13/12 Table 3: Current measurements for a parallel circuit Current (top), Current (bottom), Current (combination), I1 ( ) I2 ( ) I3 ( ) Relationship between I1, I2, and I3 B-3: Connect the voltmeter in your circuit as shown in figure 11. (Connect the voltmeter across just one of the bulbs (the top one) and measure the voltage, V1. Record the value in table 4. Draw both a schematic diagram and a sketch of the real circuit that you made. Voltmeter reading across top bulb only Schematic diagram Real circuit Without changing the voltage on the power supply, reconnect the voltmeter so it reads the voltage across the bottom bulb only, V2. Draw both a schematic diagram and a sketch of the real circuit that you made. Voltmeter reading across bottom bulb only Schematic diagram Real circuit Without changing the voltage on the power supply, reconnect the voltmeter so it reads the voltage across the power supply output, V3. This is equivalent to the voltage across the combination of both bulbs in the parallel circuit. Make sure the rest of the circuit is still attached and the light bulbs are lit when you take your reading. Draw both a schematic diagram and a sketch of the real circuit that you made. Voltmeter reading across power supply Schematic diagram Real circuit Lab: Basic Circuits Updated 09/13/12 Table 4: Voltage measurements for parallel circuit Voltage (top), Voltage (bottom), Voltage (across PS), V1 ( ) V2 ( ) V3 ( ) Relationship between V1, V2, and V3 Turn the voltage on the power supply to zero. Turn off power supply. Dismantle your circuit. Question 1 (Instead of summary/conclusion paragraph): What was the goal of, reason for, or purpose of the Basic Circuits lab? (Write your answer as if you were writing the introductory sentence to your summary/conclusion paragraph) Question 2: What do your observations of current in this lab experiment you about the relationship of current from the power supply and through the resistors in (a) series circuits and (b) parallel circuits? Question 3: What do your observations of voltage in this experiment tell you about the relationship of voltage provided by the power supply and across the resistors in (a) series circuits and (b) parallel circuits? There is no conclusion/summaryparagraph for this lab experiment. Lab: Basic Circuits Updated 09/13/12