* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C. African American
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
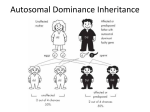
NAME _____________________________ f12 Chapter 14 -GENETIC DISORDERS TEST MODIFIED (2 points each) MATCHING: Match the genetic disorder with its description. ________ Change in hemoglobin gene causes red blood cells to change shape causing circulatory problems A. B. C. D. E. F. PHENYLKETONURIA CYSTIC FIBROSIS HUNTINGTON’s COLORBLINDNESS HEMOPHILIA SICKLE CELL DISEASE ________ Degenerative brain disorder caused by extra CAG repeats in the gene code whose symptoms appear around middle age which results in nursing home care and eventually death ________ Inability to distinguish between certain colors (especially red and green) _______ Mutation in a blood clotting protein so individuals can’t stop bleeding if injured _______ Mutation in gene that breaks down the amino acid phenylalanine which accumulates in their brain and persons become retarded if they eat foods containing phenylalanine. _______ Defect in ion channels which transport Cl- ions causing mucous to build up in lungs and digestive organs * * * _______ * * * * * * * * Mutation in muscle proteins that gradually weakens and destroys muscle tissue _______ Enzyme defect that causes lipids to build up in the brain; Results in blindness, retardation, and death by age 5 _______ Defect in bone formation resulting in a person with a normal size head and torso, but short arms and legs _______ Syndrome in which a person has an extra #21 chromosome causing mental retardation and often heart defects _______ Females with only one X chromosome (XO) _______ Males with extra X chromosomes (XXy, XXXy, XXXXy) * * * * A. TURNER SYNDROME B. DOWN SYNDROME C. TAY-SACHS D.KLINEFELTER SYNDROME E. ACHONDROPLASIA F. DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY MULTIPLE CHOICE: Tell how each of the following disorders is inherited: _______ Achondroplasia A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction ________ Sickle Cell Disease A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction _______ Hemophilia A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction ________ Tay-Sachs disease A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction _______ Down syndrome A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction ________ Colorblindness A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction _______ Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction ________ Phenylketonuria (PKU) A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction _______ Cystic Fibrosis A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction ________ Turner syndrome A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction _______ Klinefelter syndrome A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction ________ Huntington’s disease A. autosomal dominant B. autosomal recessive C. autosomal COdominant D. X-linked recessive E. nondisjunction MULTIPLE CHOICE: Put the letter of the answer that best completes the statement on the blank at the left. _______ In humans an XX genotype makes you a ___________________ A. male B. female C. D. carrier ________ ________ ________ __________________ cell mutations happen in sperm or eggs and can be passed on to the offspring. A. B. somatic C. germ D. allele ____________________ mutations cause death, often before birth. A. B. X-linked C. Germ cell D. Lethal __________________ cell mutations happen in body cells so they affect the organism itself, but are NOT passed on to offspring. A. Gamete B. Somatic C. Germ D. _______ In humans an Xy genotype makes you a ____________________. A. male B. female C. D. carrier ________ A gene that is carried on an X or Y chromosome is called ______________________. A. B. sex linked C. autosomal D. lethal ________ The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis is called ______________ A. nondisjunction B. C. crossing over D. synapsis ________ A family record that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations is called a _____________ A. karyotype B. Punnett square C. pedigree D. ________ A person that has one copy of a recessive autosomal allele and does not express the trait but can pass it on to his/her offspring is called a __________________. A. B. carrier C. hemophiliac D. gene marker ________ _______________________ can be carriers for AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE disorders. A. Only males B. Only females C. Both males and females ________ _______________________ can be carriers for X-LINKED RECESSIVE disorders. A. Only females B. Only males C. Both males and females ________ A human cell with 3 copies of a chromosome would have 47 chromosomes instead of 46. This condition is called ____________________. A. monosomy B. C. tetrads D. trisomy ________ _____________________________ twins have identical DNA. A. monozygotic B. dizygotic C. fraternal D. ________ This picture of an organism’s chromosomes is called a ______________________ A. pedigree B. Punnett square C. karyotype ________ The chromosomes that DO NOT determine sex are called ____________________ A. sex chromosomes B. autosomes C. D. pedigree partners ________ Which parent determines the sex of the baby? A. father B. mother ________ The dense region in the nucleus of female cells that forms when one of the X chromosomes is randomly inactivated is called a _____________________ body. A. autosomal B. C. nucleolus D. Barr ________ Turner syndrome is an example of a _____________________ disorder. A. trisomy B. monosomy C. somatic cell mutation ________ X-linked recessive disorders show up more frequently in ____________________. A. females B. males ________ Sickle cell disease is found more frequently in __________________________ populations. A. Jewish B. Caucasians C. African American ________ Tay-Sachs disease is found more frequently in_________________________ populations. A. B. Caucasion C. African American D. Jewish or Middle Eastern ________ Cystic fibrosis is found more frequently in _______________________ populations. A. B. Caucasion C. African American D. Jewish or Middle Eastern Match the symbol letter with the correct description Which member of this family shows the trait? A B C D E F Which represents a male is a carrier for this trait? A B C D E F A and E in the diagram above are __________________ A. normal females B. normal males C. diseased males D. diseased females B and D in the diagram above are __________________ A. normal males B. carrier males C. diseased females D. carrier females * * * * * * * * * * * * * BONUS Which genetic disorder can be found in a pedigree showing the royal families of Europe? A. Huntington’s disease B. hemophilia C. colorblindness D. Achondroplasia What trait changes in female cats as a result of the production of Barr bodies? A. length of whiskers B. length of tail C. length of hair D. spot color * *