* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Untitled
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
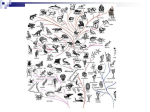
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
1 2 Artificial selection- Modifying species by selecting desired traits and breeding them. 3 Natural selection- A selection process that occurs in nature by environmental factors that allows only certain organisms to reproduce and survive. 4 Extinction- An irrevocable loss of a species. 5 6 7 Strata (layers)- The relative ages of fossils are determined by the layer on which they are found. The top layer of strata is the youngest. A fossil record provides some of the strongest evidence of evolution because of the sequence in which fossils appear within layers of rocks. Radioactive dating is also used to determine a fossils age. 8 9 Homologous structures- Features that have different functions but are structurally similar because of common ancestry. 10 Evolutionary trees show patterns of decent. 11 Gene pool- the total collection of genes in a population at any one time. Population- A group of individuals of the same species living in the same place at the same time. 12 New alleles originate by MUTATION, which is a change in nucleotide sequence of DNA. Mutation and sexual reproduction give genetic variation, making evolution possible 13 14 Types of Genetic Drift: Bottleneck effect- A drastic reduction in population size and change in allele frequencies. Founder effect- Difference in the gene pool of a small colony compared with the original population. Gene flow- where a population may gain or loose alleles when fertile individuals move into or out of a population or when gametes are transferred between populations. 15 Stabilizing direction- favors intermediate phenotypes Directional selection- Shifts the overall makeup of the population by acting against individuals at one of the phenotypic extremes. Disruptive direction- Favors individuals at both extremes of a phenotypic range. 16 17 Sexual Dimorphism- noticeable differences, not directly associated with reproduction or survival. Sexual selection- A form of natural selection in which individuals with certain characteristics are more likely than other individuals to obtain mates. Intrasexual selection- When some species secondary sex structures may be used to compete with members of the same sex for a partner. Intersexual selection- Individuals of one sex are choosy in selecting their mates. 18 19