* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download vocabulary - TeacherWeb
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Treaties between Rome and Carthage wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
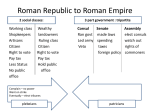
Area: around Mediterranean Sea Civilization: Roman Republic; Roman Empire vocabulary gladiator: a person trained to fight another person to the death for public entertainment arch: an upside-down U- or V-shaped structure that supports weight above it, as in a doorway vault: an arched structure used to hold up a ceiling or roof veto: to refuse to approve proposals of government made by the Senate Geography- Latins: people from the ancient country of Latinum, an area in what is now travel; the country of Italy food supply Palatine: one of the seven hills of ancient Rome Area of empire: 330 C.E.: 2 capitals: Eastern & Western Roman Empires Social plebeians: one of the common people; in the Roman Republic, a person structure & who initially had no say in government government patricians: in the Roman Republic, a rich man who held power tribune: an official of the Roman Republic elected by plebeians to protect their rights consul: one of two chief leaders in the Roman Republic Government Senate: a group of 300 men elected to govern Rome in the Roman Republic Republic: a form of government with elected leaders Empire: a large territory in which several groups of people are ruled by a single leader or government Two emperors: in 330 C.E. Emperor Constantine moved the capital of the empire to Byzantium. (Same city: Constantinople/Istanbul). Before this move emperors had shared power as co-rulers; after Constantine, power was divided between two emperors, with one based in Rome and the other in Constantinople, so Rome was the capital of just the western half of the empire. Religion Greek gods renamed: Zeus -> Jupiter, Aphrodite -> Venus, Ares -> Mars, Hermes -> Mercury, Hades -> Pluto, ... Emperors as gods: eventually worshipped as gods; other religions tolerated if they did not suggest people be disloyal to the emperor Christianity: the religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ The Arts: Realistic statues: lifelike Frescos: water-based paints on moist plaster; often showed 3-d landscapes Diverisons: Circus Maximus: racetrack; room for 200,000 spectators; chariot races; men & women allowed to sit together. Colosseum: one of the large public arenas for gladiator games. Men & women were gladiators, and fought each other or animals to the death. Men and women sat in separate sections. Technology cuniculus: an irrigation system invented by the Etruscans concrete: Romans first to make wide use of concrete, a mixture of broken stone with sand, cement, and water that was allowed to harden, making bigger arches possible. Writing & Language EconomyPhilosophy & Law Leadershipimportant people roads: built with layers of stone, sand, and gravel. Became the standard for road-building for 2000 years. aqueducts: a pipe or channel that brings water from distant places stylus: a pointed instrument used for writing Latin: English uses Latin alphabet (+ 3 other letters). Many English words from Latin. Latin prefixes: in-, im-, il- all mean not; inter = among; com- & co- mean together or with, pre = before, post = after, re = back or again, semi = half, sub = less than, trans = across Roman numerals: I = 1, V = 5, X = 10, L = 50, C = 100, D = 500, M = 1000 Stoicism: valuing a good character, having virtues such as self-control & courage. Famous for suffering bravely and quietly. Law: a legal system Justice: Romans believed in a universal law of justice that came from nature, saying all had rights. Judges tried to make fair decisions that respected people’s rights. Julius Caesar: Conquered Gaul. Civil war-against Pompey. When Caesar won-dictator for life. Senators stabbed to death on the Ides of March (15). Projects to give work: building new roads & public buildings. Kept poor happy: staging gladiator contests. Adopted new calendar. Augustus Caesar: Became emperor after Caesar assassinated & after civil war. 1st real emperor of Rome. Ruled for 41 years. Started first police force, fire fighters, & library. Expanded borders, then Pax Romana-tried for peace so could keep a strong economy. Constantine: Dreamed of Christian symbol on shields & victory. Won battle; later supported Christianity through political and economic policies. 313 C.E. 1st emperor to give Christians freedom to practice openly. 330 C.E. moved capital (see 2 emperors). On deathbed-baptized. Other points Punic Wars: Wars between Carthage & Rome. 1st: 264 – 241 B.C.E.; at of interest sea; Carthage fought for Sicily & other cities. Rome copied Carthage’s navy. Rome won. 2nd Punic War: 218 – 202 B.C.E: Hannibal crossed the alps and marched into Rome; however Scipio Africanus who attacked Carthage & won. 3rd Punic War: 149-146 B.C.E.: Rome concerned because Carthage now trading again. Carthage lost to Rome; lost all rights; ground sown with salt so nothing would grow. The Conflict of Orders: conflict between the classes: plebeians & patricians. Plebeians wanted more rights; patricians refused; plebeians marched out of Rome, refusing to work the farms and refusing to serve in the army. First strike? The Twelve Tablets: Victory for the plebeians. Laws written down so that the laws could not be changed by the patricians. 451 B.C.E. Reasons for Fall of Rome: political instability: government did not peacefully transfer power. Roman army huge, so paid for with heavy taxes-contributed to economic problems. Geography: Rome too big- surrounding Mediterranean; many potential trouble areas; many areas where tribes (Vandals, Franks, Ostrogoths, Burgundians, Gepids, Visigoths) attacked. Some tribes allowed to become part of Rome, but were never truly loyal. 330 C.E.: capital moved to Constantinople, and power split between two emperors. 410 C.E.: tribes attacked Rome itself. 476 C.E.: last emperor driven out of Rome, and western Roman empire fell.