* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
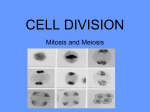
Chapter 10 and 13 Review Sheet Review Tips: Leave this sheet blank. Put your answers on a separate page so you can quiz yourself from this handout. Review ALL vocabulary Review ALL of the Notes Review ALL class handouts and worksheets. 1. The sequence of growth and division of a cell is called the _______________. Cell Cycle 2. The two phases of the cell cycle are: Interphase (G1, S, G2) and Cell division (mitosis and cytokinesis) 3. The longest phase of the cell cycle is __________________. interphase 4. Name the three phases of interphase and describe what happens in each. G1 – Gap 1 – cell is rapidly growing, performing normal duties S – Synthesis – a copy of each chromosome is made G2 – Gap 2 – cell is preparing for mitosis 5. What is created during the S phase (describe the structure). Sister chromatids – copies of a chromosome held together by a centromere 6. The process by which nuclear material is divided equally between two new cells is ________. mitosis 7. Name the four phases of mitosis and draw what each might look like. Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 8. Which phase of mitosis is the longest? prophase 9. List two things that happen during prophase in both plant and animal cells. Nuclear envelope disappears, chromatin coils up to become visible chromosomes 10. List something that happens during prophase only in animal cells. Centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell 11. Where does the spindle attach to the sister chromatids? What is the other purpose of this structure? Centromere; holds the sister chromatids together 12. How are the sister chromatids arranged during metaphase? Lined up at the equator of the cell (one sister chromatid pointed at each pole) 13. What happens to the sister chromatids during anaphase? Centromere splits and one half of each sister chromatid pair heads to an opposite pole 14. What happens in telophase? Spindle is broken down and the nuclear envelope reappears 15. Describe cytokinesis in a plant cell and in an animal cell. Animal – a furrow forms between the two new cells and it pinches together to split the two cells apart Plant – a cell plate forms between the two new cells that is eventually replaced by the cell wall 16. How do the two daughter cells compare to the original cell? They are identical 17. What controls when a cell starts the process of division (what are the types of signals)? Chemical control system Internal signals – cell senses the presence of enzymes produced within the cell External signals – cell senses the presence of chemicals (such as growth factors) produced by other specialized cells Physical signals When cells are packed in too closely, division is turned off When cells are not in contact with other cells, division is turned on 18. What happens when mitosis occurs out of control? How might the out-of-control growth of some cells affect the normal cells around them? Why does this over-growth not happen more often? Cancer Healthy cells around the cancer cells could be deprived of nutrients and/or space DNA’s repair system usually finds and corrects the errors 19. What is the primary function of DNA? Holds the information needed to make proteins 20. Put the following terms in order from smallest to largest: chromosome, DNA, and gene. DNA, gene, chromosome 21. List the three parts that make up a DNA nucleotide. Deoxyribose, phosphate group, nitrogen base (A,T,C, or G) 22. What is the process of making an exact copy of DNA called? replication 23. Where is DNA found? The nucleus of the cell 24. Where are proteins made? Ribosomes 25. How does the code from DNA get to the site of protein production? Transcription – a copy is made of a segment of DNA by RNA, a strand of mRNA brings this copy out of the nucleus and to the ribosomes to be read 26. List the three parts that make up a RNA nucleotide. Ribose, phosphate group, nitrogen base (A,U, G, or C) 27. How are the nitrogen bases different in DNA and RNA? DNA - adenine, guanine, thymine, or cytosine RNA - adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil 28. The process copying a segment of DNA using RNA to carry the message out of the nucleus is called ________________________. Transcription 29. What is a codon? A set of three nitrogen bases that code for a certain amino acid 30. The process of reading the mRNA code to make an amino acid sequence is called _________________. Translation 31. What is the job of tRNA? Brings a specific amino acid to the ribosome during translation 32. What is an anticodon? The set of three nitrogen bases on tRNA that compliment the codon on the mRNA 33. When does translation stop? When a stop codon is reached 34. What type of bonds hold amino acids together? Peptide bonds 35. What is a mutation? An error in the DNA or mRNA sequence 36. What is the difference between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation? Point – one nucleotide is replaced with an incorrect one Frameshift – one nucleotide is completely omitted causing the codon sets to be shifted and read incorrectly Be able to identify cells in each of the stages in mitosis. Be able to label the parts of a DNA molecule. Be able to identify the structures involved in translation. (pg 308) Be able to translate an mRNA sequence (try the Quick Lab on page 310) 1. Ser – arg – glu – phe – ser 2. AGA GCA, CUU, AAA, AGG 3. AGAGCACTTAAAAGG 4. TCTCGTGAATTTTCC