* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download D170 W15 Autonomic NS Williams Reading guide for lesson 12
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
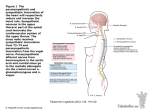
D170 W15 Autonomic NS Williams Reading guide for lesson 12 (pages 468 – 483) What are the main functions of the autonomic nervous system? What types of neurons are prevalent in the ANS? What effectors do they act on? Define the following terms: Synapse – Presynaptic neuron – Post synaptic neuron – Ganglia – Describe how the somatic motor nervous system works, including an overview of its structures. Describe how the autonomic nervous system works, including an overview of the following structures: Preganglionic neuron – Preganglionic axon (fiber) – Postganglionic neuron – Autonomic ganglion – Postganglionic axon (fiber) – D170 W15 Autonomic NS Williams What are the main functional differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions? What are the main structural differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions? What are the main biochemical differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions? Where are the cell bodies of preganglionic parasympathetic neurons found? D170 W15 Autonomic NS Williams For each of these cranial nerves, describe the parasympathetic function they have on their effectors. Oculomotor nerve (III) – Facial nerve (VII) – Glosspharyngeal nerve (IX) – Vagus nerve (X) – What nerves are involved in the sacral outflow of the parasympathetic nervous system? What organs do they innervate, and what functions do they control? Describe the basic organization of the sympathetic nervous system. What region of the spinal cord is involved? Where do the preganglionic cell bodies lie? D170 W15 Autonomic NS Describe the sympathetic trunk ganglia, noting the following structures: Sympathetic trunk – White rami communicantes – Gray rami communicantes – Superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia – Stellate ganglion – What is the difference between sympathetic trunk ganglia and dorsal root ganglia? Describe the collateral ganglia, noting the following structures: Celiac ganglia – Superior mesenteric ganglia – Inferior mesenteric ganglia – Inferior hypogastric ganglia – Williams D170 W15 Autonomic NS Williams What are the three general pathways that sympathetic preganglionic axons follow? Describe the sympathetic pathways to the periphery of the body and what functions they perform. Describe the sympathetic pathways to the head and what functions they perform. Describe the sympathetic pathways to the thoracic organs and what functions they perform. Describe the sympathetic pathways to the abdominal organs and what functions they perform. Describe the sympathetic pathways to the pelvic organs and what functions they perform. D170 W15 Autonomic NS Explain the role of the adrenal medulla in the sympathetic division. Describe the role and location of visceral sensory neurons relative to autonomic neurons. What is referred pain? What is a visceral reflex arc? What are some examples? Williams