Dysphagia in the Elderly
... but they are frequently the cause of dysphagia. Many elderly persons presenting with dysphagia are unaware of aspiration. When silent aspiration, often associated with vascular lesions in the basal ganglia, occurs repeatedly during ...
... but they are frequently the cause of dysphagia. Many elderly persons presenting with dysphagia are unaware of aspiration. When silent aspiration, often associated with vascular lesions in the basal ganglia, occurs repeatedly during ...
Document
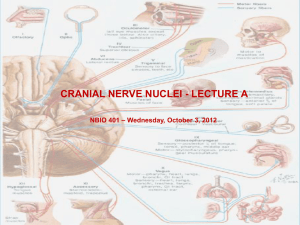
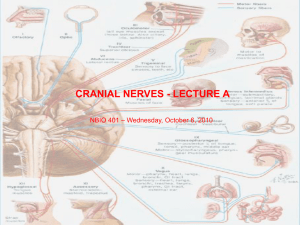
... Objective for the first two cranial nerve lectures, those about cranial nerve nuclei: ...
... Objective for the first two cranial nerve lectures, those about cranial nerve nuclei: ...
The Peripheral Nervous System - Advanced
... The components of a reflex. A sensory receptor detects a stimulus and sends nerve signals to the spinal cord. These signals activate motor neurons that lead back to the effector (muscle). ...
... The components of a reflex. A sensory receptor detects a stimulus and sends nerve signals to the spinal cord. These signals activate motor neurons that lead back to the effector (muscle). ...
Transcripts/3_9 1
... f. Nucleus of ambiguous also provides output. XIII. Visceral and Somatic Afferents [S13] a. You have sensory information coming in from the somatic sensory neurons and visceral sensory neurons and they are both are coming into the dorsal horn neurons. Early evidence that their projections to the rel ...
... f. Nucleus of ambiguous also provides output. XIII. Visceral and Somatic Afferents [S13] a. You have sensory information coming in from the somatic sensory neurons and visceral sensory neurons and they are both are coming into the dorsal horn neurons. Early evidence that their projections to the rel ...
neurology part1_lab10_10_5_2011
... pterygopalatine ganglion ((to the lacrimal gland)) &submandibular ganglion ((to submandibular gland & sublingual gland)) The passage of facial nerve outside the cranial cavity through the internal auditory meatus then outside the skull through stylomastoid foramen through the parotid gland it’ll div ...
... pterygopalatine ganglion ((to the lacrimal gland)) &submandibular ganglion ((to submandibular gland & sublingual gland)) The passage of facial nerve outside the cranial cavity through the internal auditory meatus then outside the skull through stylomastoid foramen through the parotid gland it’ll div ...
Table 14.2 - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... excited by either an external stretch or an internal stretch The Golgi tendon reflex produces muscle relaxation and lengthening in response to contraction The flexor, or withdrawal, reflex is initiated by a painful stimulus and causes automatic withdrawal of the threatened body part from the stimulu ...
... excited by either an external stretch or an internal stretch The Golgi tendon reflex produces muscle relaxation and lengthening in response to contraction The flexor, or withdrawal, reflex is initiated by a painful stimulus and causes automatic withdrawal of the threatened body part from the stimulu ...
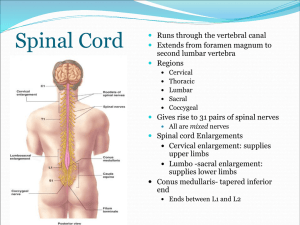
Spinal Cord
... and progressive weakness of her right lower limb for a period of two months, she contacted her Family physician, Her Family physician referred her to a neurologist. The neurologic evaluation revealed weakness in the right lower limb. This was associated with spasticity (increased tone), hyperrefle ...
... and progressive weakness of her right lower limb for a period of two months, she contacted her Family physician, Her Family physician referred her to a neurologist. The neurologic evaluation revealed weakness in the right lower limb. This was associated with spasticity (increased tone), hyperrefle ...
D170 W15 Autonomic NS Williams Reading guide for lesson 12
... For each of these cranial nerves, describe the parasympathetic function they have on their effectors. Oculomotor nerve (III) – Facial nerve (VII) – Glosspharyngeal nerve (IX) – Vagus nerve (X) – ...
... For each of these cranial nerves, describe the parasympathetic function they have on their effectors. Oculomotor nerve (III) – Facial nerve (VII) – Glosspharyngeal nerve (IX) – Vagus nerve (X) – ...
Gross Anatomy Lecture 1: Spinal Cord and Nerves I. Basic
... 1. Voluntary – sensory info can be evaluated at higher centers such as cortex to formulate conscious (voluntary) motor plan to guide desired response a. Ex picking up glass of water b. Sensory limb spinal cord cortex spinal cord motor limb 2. Reflex - rapid involuntary movement in response to ...
... 1. Voluntary – sensory info can be evaluated at higher centers such as cortex to formulate conscious (voluntary) motor plan to guide desired response a. Ex picking up glass of water b. Sensory limb spinal cord cortex spinal cord motor limb 2. Reflex - rapid involuntary movement in response to ...
Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... spinal cord. It is so important that, if it is severely compromised, the victim will likely die. The medulla oblongata is a relay station, house for cranial nerve nuclei, and most importantly, controls visceral functions like blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate. ...
... spinal cord. It is so important that, if it is severely compromised, the victim will likely die. The medulla oblongata is a relay station, house for cranial nerve nuclei, and most importantly, controls visceral functions like blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate. ...
I. Overview - El Camino College
... body epithelium; excess drains through the canal of __________; excess fluid causes ___________. The anterior cavity is further divided into: 1) ____________ chamber - between the cornea & iris 2) ____________ chamber - between the iris & lens 5. Other visual pathways include optic tracts to the: a. ...
... body epithelium; excess drains through the canal of __________; excess fluid causes ___________. The anterior cavity is further divided into: 1) ____________ chamber - between the cornea & iris 2) ____________ chamber - between the iris & lens 5. Other visual pathways include optic tracts to the: a. ...
L4-As.Tracts 2014 (final).
... • Carry impulses concerned with proprioception (movement and joint position) and discriminative touch from ipsilateral side of the body • Contain the axons of primary afferent neurons that have entered cord through dorsal roots of spinal nerves • Fasciculus Gracilis contains fibers that are received ...
... • Carry impulses concerned with proprioception (movement and joint position) and discriminative touch from ipsilateral side of the body • Contain the axons of primary afferent neurons that have entered cord through dorsal roots of spinal nerves • Fasciculus Gracilis contains fibers that are received ...
3-As.Tracts 2014 (final).
... • Carry impulses from pain, thermal, tactile, muscle and joint receptors to the brain. • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (at the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g at the cerebellum). ...
... • Carry impulses from pain, thermal, tactile, muscle and joint receptors to the brain. • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (at the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g at the cerebellum). ...
3-As.Tracts 2016-17
... contact with the second neurone which lies either in the spinal grey matter or in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem. ...
... contact with the second neurone which lies either in the spinal grey matter or in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem. ...
3-As.Tracts 2015 (final).
... Leads to loss of proprioseption which is manifested by a high steppage and unsteady gait (sensory ataxia) ...
... Leads to loss of proprioseption which is manifested by a high steppage and unsteady gait (sensory ataxia) ...
Neuroanatomy/Pain Review
... Any pain which lasts for six months or more (in athletes we may consider chronic pain to be pain which is continue from months but is not in proportion to tissue injury or activity... i.e... chronic tendinitis may be long lasting but have organic root) No real purpose (?) numerous by-passes. Also ...
... Any pain which lasts for six months or more (in athletes we may consider chronic pain to be pain which is continue from months but is not in proportion to tissue injury or activity... i.e... chronic tendinitis may be long lasting but have organic root) No real purpose (?) numerous by-passes. Also ...
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Monosynaptic reflex arc. Ipsilateral reflex. This reflex helps avert injury by preventing overstretching of a muscle. Reciprocal inhibition – when the stretched muscle contracts, the antagonistic muscle(s) relax. ...
... Monosynaptic reflex arc. Ipsilateral reflex. This reflex helps avert injury by preventing overstretching of a muscle. Reciprocal inhibition – when the stretched muscle contracts, the antagonistic muscle(s) relax. ...
Spinal and Cranial Nerves
... • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera • Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera ...
... • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera • Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera ...
TSM7 - Somatosensory Pathways
... o Second order neurons decussate to the contralateral side and group together At the thalamus they converge at the ventral posterior lateral nucleus (VPL) The sensory information finally reaches the primary somatosensory cortex (PSSC) ...
... o Second order neurons decussate to the contralateral side and group together At the thalamus they converge at the ventral posterior lateral nucleus (VPL) The sensory information finally reaches the primary somatosensory cortex (PSSC) ...
Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system
... b) Bones of the skull and shoulder blades are flat. c) The spine is composed of regular-shaped bones. d) The rounded end of a long bone is called epiphysis. e) Flat bones are made up of two layers of spongy bone. f) The tibia is an example of a long bone. g) Short bones are found in the fingers and ...
... b) Bones of the skull and shoulder blades are flat. c) The spine is composed of regular-shaped bones. d) The rounded end of a long bone is called epiphysis. e) Flat bones are made up of two layers of spongy bone. f) The tibia is an example of a long bone. g) Short bones are found in the fingers and ...