* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Descriptor
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
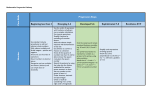
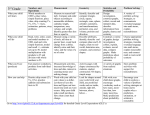
Understanding your Foundation AQA Linear Specification using the AQA Modular books This table will show you exactly where to find all the content that you require to complete your Foundation AQA Linear Specification using the Collins New GCSE Maths AQA Modular books. Descriptor Core and Recall Unit 1 Unit 2 Number N1.1 Understand integers and place value to deal with arbitrary large positive numbers Add, subtract, multiply and divide any number. N1.2 N1.3 N1.4 N1.5 N1.6 Understand and use number operations and the relationships between them, including inverse operations and hierarchy of operations. Approximate to a given power of 10, up to three decimal places and one significant figure. Order rational numbers. Book 1, lesson 1.4 Book 1, lessons 1.1, 1.2, 1.6, 1.7, 3.2, 3.4 Book 1, lessons 1.3, 3.2, 3.3 Book 2, lesson 1.1 Book 1, lesson 1.5 Book 1, lesson 11.1, 11.2, 11.3, 11.4 Book 1, lesson 11.3, 11.5 Book 1 lessons 2.10, 3.1 The concepts and vocabulary of factor (divisor), multiple, common factor, highest common factor, least common multiple, prime number and prime factor decomposition. The terms square, positive and negative square root, cube and cube root. N1.7 Index notation for squares, cubes and powers of 10. N1.8 N1.9 N1.14 Index laws for multiplication and division of integer powers. Use a calculator effectively and efficiently. Book 1 and Book 2 throughout Book 2, lesson 11.1 Book 1, lesson 4.1 Book 1, lessons 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, Book 1, lessons 9.4, 9.5, 9.6, 9.8 Book 1, lessons 9.4, 9.5, 9.6 Book 1, lesson 9.6, 9.7, 9.9 Unit 3 N2.1 Understand equivalent fractions, simplifying a fraction by cancelling all common factors. Book 1, lessons 2.1 – 2.4 Add and subtract fractions. Book 1 lessons 2.2, 2.5, 2.6 Book 2 lesson 1.2 Book 1 lesson 2.10 N2.2 N2.3 N2.4 N2.5 Use decimal notation and recognise that each terminating decimal is a fraction. Recognise that recurring decimals are exact fractions and that some exact fractions are recurring decimals. Understand that ‘percentage’ means ‘number of parts per 100’ and use this to compare proportions. Interpret fractions, decimals and percentages as operators. N2.6 Calculate with fractions, decimals and percentages as operators. N2.7 N3.1 N3.2 N3.3 Use ratio notation, including reduction to its simplest form and its various links to fraction notation. Divide a quantity in a given ratio. Book 1, lesson 2.10 Book 1, lesson 4.1 Book 1, lessons 4.1, 4.2 Book 2 lesson 1.3 Book 1 lessons 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 4.3, 4.4 Book 2 lesson 1.3 Book 1 lesson 4.5 Book 1, lessons 2.4, 4.2, 5.3 Book 1, lesson 4.3 Book 1, lesson 1.1 Book 1, lesson 4.3 Book 1, lessons 1.4, 5.5 Book 1, lesson 11.3 Book 1 lesson 4.5 Solve problems involving ratio and proportion, including the unitary method of solution. Book 1 lesson 4.5 Distinguish the different roles played by letter symbols in algebra, using the correct notation. Distinguish in meaning between the words ‘equation’, ‘formula’, and ‘expression’. Manipulate algebraic expressions by collecting like terms, by multiplying a single term over a bracket, and by taking out common factors. Book 2, lesson 2.1 Book 2 lessons 5.1 – 5.3 Algebra N4.1 N4.2 N5.1 Book 2, lesson 2.1 Book 2, lesson 2.1 Book 1, lesson 10.1 Book 1, lesson 10.1 Book 1, lessons 10.2 – 10.4 Set up and solve simple linear equations. Book 2, lessons 2.3, 2.4 Derive a formula, substitute numbers into a formula and change the subject of a formula Book 2, lesson 2.2 N5.4 N5.6 N5.7 N5.8 Solve linear inequalities in one variable and represent the solution set on a number line. Use systematic trial and improvement to find approximate solutions of equations where there is no simple analytical method of solving them. Use algebra to support and construct arguments. N5.9 N6.1 N6.2 Generate terms of a sequence using term-to-term and position to term definitions of the sequence. Use linear expressions to describe the nth term of an arithmetic sequence. N6.3 Use the conventions for coordinates in the plane and plot points in all four quadrants, including using geometric information. N6.4 Recognise and plot equations that correspond to straight-line graphs in the coordinate plane, including finding their gradients. N6.11 Construct linear functions from real-life problems and plot their corresponding graphs. N6.12 Discuss, plot and interpret graphs (which may be non-linear) modelling real situations. Generate points and plot graphs of simple quadratic functions, and use these to find approximate solutions. Geometry Recall and use properties of angles at a point, angles at a point on a G1.1 N6.13 Book 1, lessons 12.1 – 12.3 Book 1, lessons 10.5, 12.4 Book 1, lesson 12.5 Book 2, lesson 2.5 Book 1 Chapters 10, 12 Book 1, lessons 14.1, 14.2, 14.4 Book 1, lesson 14.3, 14.4 Book 1, lesson 13.3 Book 1, lessons 13.3, 13.4 Book 1, lessons 13.1, 13.2 Book 1, lessons 13.1, 13.2 Book 2, lesson 13.1 Book 2, lesson 13.1 Book 2, G1.2 straight line (including right angles), perpendicular lines and opposite angles at a vertex. Understand and use the angle properties of parallel and intersecting lines, triangles and quadrilaterals. G1.3 Calculate and use the sums of the interior and exterior angles of polygons. G1.4 G1.5 Recall the properties and definitions of special types of quadrilateral, including square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezium, kite and rhombus. Distinguish between centre, radius, chord, diameter, circumference, tangent, arc, sector and segment. Recognise reflection and rotation symmetry of 2D shapes. G1.6 G1.7 Describe and transform 2D shapes using single or combined rotations, reflections, translations, or enlargements by a positive scale factor and distinguish properties that are preserved under particular transformations. G1.8 Understand congruence and similarity. Use Pythagoras’ theorem. G2.1 Justify simple geometrical properties. G2.3 Use 2D representations of 3D shapes. G2.4 Use and interpret maps and scale drawings. G3.1 G3.2 Understand the effects of enlargement for perimeter, area and for volume of shapes and solids. lesson 8.2 Book 2, lessons 8.3, 8.4, 8.6 Book 2, lessons 8.4, 8.5 Book 2, lesson 8.7 Book 2, lesson 9.1 Book 2, lessons 7.1, 7.2, 10.4, 10.5 Book 2, lessons 10.2 – 10.6 Book 2, lesson 10.1 Book 2, lessons 14.1 – 14.3 Throughout Geometry chapters Book 2, lessons 4.4, 4.5 Book 2, lessons 4.2, 4.3 Book 2, lesson 10.6 G3.3 Interpret scales on a range of measuring instruments and recognise the inaccuracy of measurements. Convert measurements from one unit to another. Book 2, lesson 4.1 Book 2, lessons 3.2 3.4 Book 2, lessons 3.1, 4.2 Book 2, lesson 8.8 Book 2, lesson 5.1 Book 2, lessons 3.8, 9.1, 11.1 Book 2, lesson 11.1 Book 2, lesson 11.2 Book 2, lesson 11.3 Book 2, lessons 6.16.7, 12.2 – 12.4 Book 2, lessons 9.2 – 9.4 Book 2, lessons 12.1 – 12.4 Book 2, lesson 10.3 G3.4 Make sensible estimates of a range of measures. G3.5 G3.6 G3.7 Understand and use bearings. Understand and use compound measures. Measure and draw lines and angles. G3.8 G3.9 G3.10 G3.11 G4.1 Draw triangles and other 2D shapes using a ruler and protractor. Use straight edge and a pair of compasses to do constructions. Construct loci. Calculate perimeters and areas of shapes made from triangles and rectangles. Calculate circumference and areas of circles. G4.3 G4.4 G5.1 Calculate volumes of right prisms and of shapes made from cubes and cuboids Understand and use vector notation for translations. Statistics Understand and use the statistical problem solving process which S1 Book 1 , S2.1 S2.2 S2.3 S2.4 involves • specifying the problem and planning • collecting data • processing and presenting the data • interpreting and discussing the results. Types of data: qualitative, discrete, continuous. Use of grouped and ungrouped data. Identify possible sources of bias. Design an experiment or survey. Design data-collection sheets distinguishing between different types of data. Extract data from printed tables and lists. S2.5 S3.1 S3.2 Design and use two-way tables for grouped and ungrouped data. Produce charts and diagrams for various data types. Scatter graphs, stem-and-leaf, tally charts, pictograms, bar charts, dual bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, frequency polygons, histograms with equal class intervals. Calculate median, mean, range, mode and modal class. S3.3 Interpret a wide range of graphs and diagrams and draw conclusions. S4.1 S4.2 S4.3 S4.4 Look at data to find patterns and exceptions Recognise correlation and draw and/or use lines of best fit by eye, understanding what they represent. Compare distributions and make inferences. lesson 8.4 Book 1, lesson 8.4 Book 1, lesson 8.4 Book 1, lesson 8.3 Book 1, lesson 8.3 Book 1, lessons 5.1 – 5.4, 6.1 – 6.7 Book 1, lesson 7.8 Book 1, lessons 5.1 – 5.4, 6.8, 8.1, 8.2, 8.5 Book 1, lessons 6.1 – 6.7 Book 1, lessons 5.1 – 5.4, 6.8, 8.1, Book 1, lesson 8.2 Book 1, lesson 8.2 Book 1, lesson 8.2 S5.2 Understand and use the vocabulary of probability and the probability scale. Understand and use estimates or measures of probability from theoretical models (including equally likely outcomes), or from relative frequency. S5.3 List all outcomes for single events, and for two successive events, in a systematic way and derive related probabilities. S5.4 Identify different mutually exclusive outcomes and know that the sum of the probabilities of all these outcomes is 1. S5.1 S5.7 Compare experimental data and theoretical probabilities. S5.8 Understand that if an experiment is repeated, this may – and usually will – result in different outcomes. S5.9 Understand that increasing sample size generally leads to better estimates of probability and population characteristics. Book 1, lesson 7.1 Book 1, lessons 7.2, 7.4, 7.5, 7.7 Book 1, lessons 7.4, 7.6, 7.8 Book 1, lessons 7.3, 7.4 Book 1, lesson 7.5 Book 1, lessons 7.5, 8.4 Book 1, lessons 7.5, 8.4